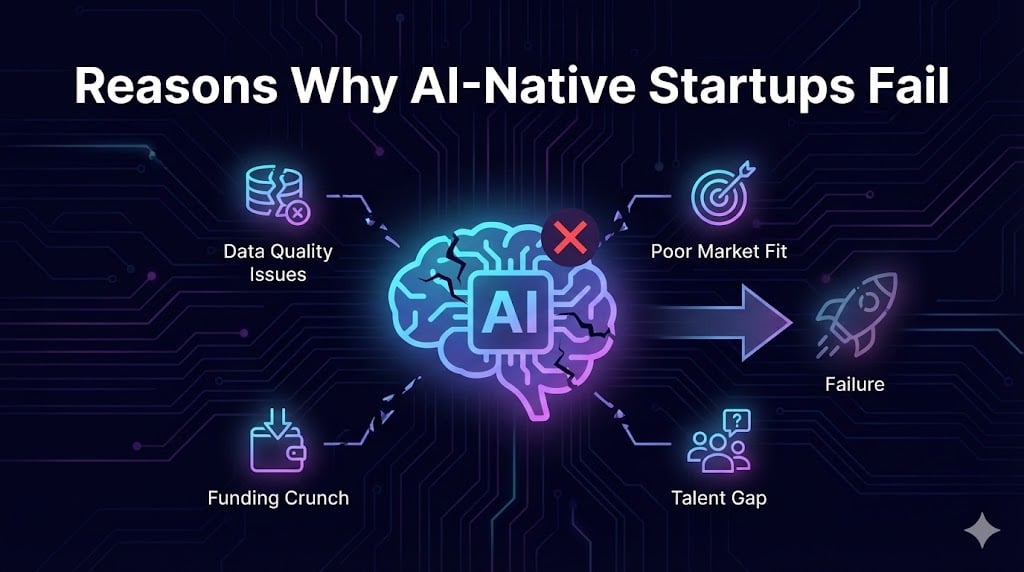
Synthetic intelligence startups have captured traders’ imaginations, however most fail inside a number of years. Research in 2025–26 present that roughly 90 % of AI‑native startups fold inside their first yr, and even enterprise AI pilots have a 95 % failure charge. These numbers reveal a startling hole between the promise of AI and its actual‑world implementation.
To grasp why, this text dissects the important thing causes AI startups fail and gives actionable methods. All through the article, Clarifai’s compute orchestration, mannequin inference and native runner options are featured as an example how the proper infrastructure decisions can shut many of those gaps.
Fast Digest: What You’ll Be taught
- Why failure charges are so excessive – Knowledge from a number of stories present that over 80 % of AI tasks by no means make it previous proof of idea. We discover why hype and unrealistic expectations produce unsustainable ventures.
- The place most startups misfire – Poor product‑market match accounts for over a 3rd of AI startup failures; we look at the way to discover actual buyer ache factors.
- The hidden prices of AI infrastructure – GPU shortages, lengthy‑time period cloud commitments and escalating compute payments can kill startups earlier than launch. We focus on price‑environment friendly compute methods and spotlight how Clarifai’s orchestration platform helps.
- Knowledge readiness and high quality challenges – Poor information high quality and lack of AI‑prepared information trigger greater than 30 % of generative AI tasks to be deserted; we define sensible information governance practices.
- Regulatory, moral and environmental hurdles – We unpack the regulatory maze, compliance prices and vitality‑consumption challenges dealing with AI corporations, and present how startups can construct belief and sustainability into their merchandise.
Why do AI startups fail regardless of the hype?
Fast Abstract
Query: Why are failure charges amongst AI‑native startups so excessive?
Reply: A mixture of unrealistic expectations, poor product‑market match, inadequate information readiness, runaway infrastructure prices, dependence on exterior fashions, management missteps, regulatory complexity, and vitality/useful resource constraints all contribute to extraordinarily excessive failure charges.
The wave of pleasure round AI has led many founders and traders to equate know-how prowess with a viable enterprise mannequin. Nevertheless, the MIT NANDA report on the state of AI in enterprise (2025) discovered that solely about 5 % of generative AI pilots obtain speedy income development, whereas the remaining 95 % stall as a result of instruments fail to study from organisational workflows and budgets are misallocated towards hype‑pushed tasks fairly than again‑workplace automation.
Professional insights:
- Studying hole over know-how hole – The MIT report emphasizes that failures come up not from mannequin high quality however from a “studying hole” between AI instruments and actual workflows; off‑the‑shelf instruments don’t adapt to enterprise contexts.
- Lack of clear drawback definition – RAND’s research of AI tasks discovered that misunderstanding the issue to be solved and specializing in the most recent know-how as an alternative of actual person wants have been main causes of failure.
- Useful resource misallocation – Greater than half of AI budgets go to gross sales and advertising and marketing instruments although the largest ROI lies in again‑workplace automation.
Overestimating AI capabilities: the hype vs actuality drawback
Fast Abstract
Query: How do unrealistic expectations derail AI startups?
Reply: Founders usually assume AI can resolve any drawback out‑of‑the‑field and underestimate the necessity for area information and iterative adaptation. They mistake “AI‑powered” branding for a sustainable enterprise and waste assets on demos fairly than fixing actual ache factors.
Many early AI ventures wrap generic fashions in a slick interface and market them as revolutionary. An influential essay describing “LLM wrappers” notes that the majority so‑known as AI merchandise merely name exterior APIs with exhausting‑coded prompts and cost a premium for capabilities anybody can reproduce. As a result of these instruments have no proprietary information or infrastructure, they lack defensible IP and bleed money when utilization scales.
- Know-how chasing vs drawback fixing – A typical anti‑sample is constructing spectacular fashions with no clear buyer drawback, then trying to find a market afterwards.
- Misunderstanding AI’s limitations – Stakeholders might imagine present fashions can autonomously deal with advanced choices; in actuality, AI nonetheless requires curated information, area experience and human oversight. RAND’s survey reveals that making use of AI to issues too tough for present capabilities is a serious reason behind failure.
- “Demo lure” – Some startups spend hundreds of thousands on flashy demos that generate press however ship little worth; about 22 % of startup failures stem from inadequate advertising and marketing methods and communication.
Professional insights:
- Specialists advocate constructing small, focused fashions fairly than over‑committing to giant basis fashions. Smaller fashions can ship 80 % of the efficiency at a fraction of the associated fee.
- Clarifai’s orchestration platform makes it simple to deploy the proper mannequin for every process, whether or not a big foundational mannequin or a light-weight customized community. Compute orchestration lets groups check and scale fashions with out over‑provisioning {hardware}.
Inventive instance:
Think about launching an AI‑powered observe‑taking app that prices $50/month to summarize conferences. With out proprietary coaching information or distinctive algorithms, the product merely calls an exterior API. Customers quickly uncover they’ll replicate the workflow themselves for a number of {dollars} and abandon the subscription. A sustainable various could be to coach area‑particular fashions on proprietary assembly information and provide distinctive analytics; Clarifai’s platform can orchestrate this at low price.
The product‑market match lure: fixing non‑existent issues
Fast Abstract
Query: Why does poor product‑market match topple AI startups?
Reply: Thirty‑4 % of failed startups cite poor product‑market match as the first perpetrator. Many AI ventures construct know-how first and seek for a market later, leading to merchandise that don’t resolve actual buyer issues.
- Market demand vs innovation – 42 % of startups fail as a result of there isn’t a market demand for his or her product. AI founders usually fall into the lure of making options in the hunt for an issue.
- Actual‑world case research – A number of excessive‑profile shopper robots and generative artwork instruments collapsed as a result of shoppers discovered them gimmicky or overpriced. One other startup spent hundreds of thousands coaching a picture generator however hardly invested in buyer acquisition, leaving them with fewer than 500 customers.
- Underestimating advertising and marketing and communication – 22 % of failed startups falter because of inadequate advertising and marketing and communication methods. Complicated AI options want clear messaging to convey worth.
Professional insights:
- Begin with ache, not know-how – Profitable founders establish a excessive‑worth drawback and design AI to unravel it. This implies conducting person interviews, validating demand and iterating rapidly.
- Cross‑purposeful groups – Constructing interdisciplinary groups combining technical expertise with product managers and area specialists ensures that know-how addresses precise wants.
- Clarifai integration – Clarifai permits speedy prototyping and person testing by a drag‑and‑drop interface. Startups can construct a number of prototypes, check them with potential prospects, and refine till product‑market match is achieved.
Inventive instance:
Suppose an AI startup desires to create an automatic authorized assistant. As an alternative of instantly coaching a big mannequin on random authorized paperwork, the group interviews legal professionals to seek out out that they spend numerous hours redacting delicate data from contracts. The startup then makes use of Clarifai’s pretrained fashions for doc AI, builds a customized pipeline for redaction, and checks it with customers. The product solves an actual ache level and features traction.
Knowledge high quality and readiness: gasoline or failure for AI
Knowledge is the gasoline of AI. Nevertheless, many organizations misread the issue as “not sufficient information” when the actual difficulty is not sufficient AI‑prepared information. AI‑prepared information have to be match for the particular use case, consultant, dynamic, and ruled for privateness and compliance.
- Knowledge high quality and readiness – Gartner’s surveys present that 43 % of organizations cite information high quality and readiness as the highest impediment in AI deployments. Conventional information administration frameworks are usually not sufficient; AI requires contextual metadata, lineage monitoring and dynamic updating.
- Dynamic and contextual information – Not like enterprise analytics, AI use instances change always; information pipelines have to be iterated and ruled in actual time.
- Consultant and ruled information – AI‑prepared information could embrace outliers and edge instances to coach strong fashions. Governance should meet evolving privateness and compliance requirements.
Professional insights:
- Put money into information foundations – RAND recommends investing in information governance infrastructure and mannequin deployment to scale back failure charges.
- Clarifai’s information workflows – Clarifai gives built-in annotation instruments, information governance, and mannequin versioning that assist groups accumulate, label and handle information throughout the lifecycle.
- Small information, sensible fashions – When information is scarce, strategies like few‑shot studying, switch studying and retrieval‑augmented era (RAG) can construct efficient fashions with restricted information. Clarifai’s platform helps these approaches.
Fast Abstract
How does information readiness decide AI startup success?
Poor information high quality and lack of AI‑prepared information are among the many high causes AI tasks fail. Not less than 30 % of generative AI tasks are deserted after proof of idea due to poor information high quality, insufficient danger controls and unclear enterprise worth.
Infrastructure and compute prices: hidden black holes
Fast Abstract
Query: Why do infrastructure prices cripple AI startups?
Reply: AI isn’t only a software program drawback—it’s basically a {hardware} problem. Huge GPU processing energy is required to coach and run fashions, and the prices of GPUs might be as much as 100× larger than conventional computing. Startups incessantly underestimate these prices, lock themselves into lengthy‑time period cloud contracts, or over‑provision {hardware}.
The North Cloud report on AI’s price disaster warns that infrastructure prices create “monetary black holes” that drain budgets. There are two forces behind the issue: unknown compute necessities and world GPU shortages. Startups usually decide to GPU leases earlier than understanding precise wants, and cloud suppliers require long-term reservations because of demand. This leads to overpaying for unused capability or paying premium on-demand charges.
- Coaching vs manufacturing budgets – With out separate budgets, groups burn by compute assets throughout R&D earlier than proving any enterprise worth.
- Price intelligence – Many organizations lack programs to trace the price per inference; they solely discover the invoice after deployment.
- Begin small and scale slowly – Over‑committing to giant basis fashions is a typical mistake; smaller process‑particular fashions can obtain related outcomes at decrease price.
- Versatile GPU commitments – Negotiating moveable commitments and utilizing native runners can mitigate lock‑in.
- Hidden information preparation tax – Startups journal notes that information preparation can eat 25–40 % of the price range even in optimistic eventualities.
- Escalating operational prices – Enterprise‑backed AI startups usually see compute prices develop at 300 % yearly, six instances larger than non‑AI SaaS counterparts.
Professional insights:
- Use compute orchestration – Clarifai’s compute orchestration schedules workloads throughout CPU, GPU and specialised accelerators, making certain environment friendly utilization. Groups can dynamically scale compute up or down based mostly on precise demand.
- Native runners for price management – Operating fashions on native {hardware} or edge units reduces dependence on cloud GPUs and lowers latency. Clarifai’s native runner framework permits safe on‑prem deployment.
- Separate analysis and manufacturing – Maintaining R&D budgets separate from manufacturing budgets forces groups to show ROI earlier than scaling costly fashions..
Inventive instance:
Contemplate an AI startup constructing a voice assistant. Early prototypes run on a developer’s native GPU, however when the corporate launches a beta model, utilization spikes and cloud payments soar to $50,000 monthly. With out price intelligence, the group can’t inform which options drive consumption. By integrating Clarifai’s compute orchestration, the startup measures price per request, throttles non‑important options, and migrates some inference to edge units, reducing month-to-month compute by 60 %.
The wrapper drawback: dependency on exterior fashions
Fast Abstract
Query: Why does reliance on exterior fashions and APIs undermine AI startups?
Reply: Many AI startups construct little greater than skinny wrappers round third‑celebration giant language fashions. As a result of they management no underlying IP or information, they lack defensible moats and are weak to platform shifts. As one evaluation factors out, these wrappers are simply immediate pipelines stapled to a UI, with no backend or proprietary IP.
- No differentiation – Wrappers rely completely on exterior mannequin suppliers; if the supplier adjustments pricing or mannequin entry, the startup has no recourse.
- Unsustainable economics – Wrappers burn money on freemium customers, however nonetheless pay the supplier per token. Their enterprise mannequin hinges on changing customers quicker than burn, which not often occurs.
- Brittle distribution layer – When wrappers fail, the underlying mannequin supplier additionally loses distribution. This round dependency creates systemic danger.
Professional insights:
- Construct proprietary information and fashions – Startups must personal their coaching information or develop distinctive fashions to create lasting worth.
- Use open fashions and native inference – Clarifai gives open‑weight fashions that may be positive‑tuned regionally, lowering dependence on any single supplier.
- Leverage hybrid architectures – Combining exterior APIs for generic duties with native fashions for area‑particular features offers flexibility and management.
Management, tradition and group dynamics
Fast Abstract
Query: How do management and tradition affect AI startup outcomes?
Reply: Lack of strategic alignment, poor government sponsorship and inner resistance to vary are main causes of AI undertaking failure. Research report that 85 % of AI tasks fail to scale because of management missteps. With out cross‑purposeful groups and a tradition of experimentation, even properly‑funded initiatives stagnate.
- Lack of C‑suite sponsorship – Tasks with no dedicated government champion usually lack assets and route.
- Unclear enterprise goals and ROI – Many AI initiatives launch with obscure objectives, resulting in scope creep and misaligned expectations.
- Organizational inertia and worry – Workers resist adoption because of worry of job displacement or lack of information.
- Siloed groups – Poor collaboration between enterprise and technical groups leads to fashions that don’t resolve actual issues.
Professional insights:
- Empower line managers – MIT’s analysis discovered that profitable deployments empower line managers fairly than central AI labs.
- Domesticate interdisciplinary groups – Combining information scientists, area specialists, designers and ethicists fosters higher product choices.
- Incorporate human‑centered design – Clarifai advocates constructing AI programs with the top person in thoughts; person expertise ought to information mannequin design and analysis.
- Embrace steady studying – Encourage a development mindset and supply coaching to upskill workers in AI literacy.
Regulatory and moral hurdles
Fast Abstract
Query: How does the regulatory panorama have an effect on AI startups?
Reply: Greater than 70 % of IT leaders record regulatory compliance as a high problem when deploying generative AI. Fragmented legal guidelines throughout jurisdictions, excessive compliance prices and evolving moral requirements can sluggish and even halt AI tasks.
- Patchwork rules – New legal guidelines such because the EU AI Act, Colorado’s AI Act and Texas’s Accountable AI Governance Act mandate danger assessments, impression evaluations and disclosure of AI utilization, with fines as much as $1 million per violation.
- Low confidence in governance – Fewer than 25 % of IT leaders really feel assured managing safety and governance points. The complexity of definitions like “developer,” “deployer” and “excessive danger” causes confusion.
- Danger of authorized disputes – Gartner predicts AI regulatory violations will trigger a 30 % enhance in authorized disputes by 2028.
- Small corporations in danger – Compliance prices can vary from $2 million to $6 million per agency, disproportionately burdening startups.
Professional insights:
- Early governance frameworks – Set up inner insurance policies for ethics, bias evaluation and human oversight. Clarifai gives instruments for content material moderation, security classification, and audit logging to assist corporations meet regulatory necessities.
- Automated compliance – Analysis suggests future AI programs may automate many compliance duties, lowering the commerce‑off between regulation and innovation. Startups ought to discover compliance‑automating AIs to remain forward of rules.
- Cross‑jurisdiction technique – Interact authorized specialists early and construct a modular compliance technique to adapt to completely different jurisdictions.
Sustainability and useful resource constraints: the AI‑vitality nexus
Fast Abstract
Query: What position do vitality and assets play in AI startup viability?
Reply: AI’s speedy development locations monumental pressure on vitality programs, water provides and important minerals. Knowledge centres are projected to eat 945 TWh by 2030—greater than double their 2024 utilization. AI may account for over 20 % of electrical energy demand development, and water utilization for cooling is predicted to succeed in 450 million gallons per day. These pressures can translate into rising prices, regulatory hurdles and reputational dangers for startups.
- Power consumption – AI’s vitality urge for food ties startups to unstable vitality markets. With out renewable integration, prices and carbon footprints will skyrocket.
- Water stress – Most information centres function in excessive‑stress water areas, creating competitors with agriculture and communities.
- Essential minerals – AI {hardware} depends on minerals similar to cobalt and uncommon earths, whose provide chains are geopolitically fragile.
- Environmental and neighborhood impacts – Over 1,200 mining websites overlap with biodiversity hotspots. Poor stakeholder engagement can result in authorized delays and reputational injury.
Professional insights:
- Inexperienced AI practices – Undertake vitality‑environment friendly mannequin architectures, prune parameters and use distillation to scale back vitality consumption. Clarifai’s platform offers mannequin compression strategies and permits operating fashions on edge units, lowering information‑centre load.
- Renewable and carbon‑conscious scheduling – Use compute orchestration that schedules coaching when renewable vitality is plentiful. Clarifai’s orchestration can combine with carbon‑conscious APIs.
- Lifecycle sustainability – Design merchandise with sustainability metrics in thoughts; traders more and more demand environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting.
Operational self-discipline, advertising and marketing and execution
Fast Abstract
Query: How do operational practices affect AI startup survival?
Reply: Past technical excellence, AI startups want disciplined operations, monetary administration and efficient advertising and marketing. AI startups burn by capital at unprecedented charges, with some burning $100 million in three years. With out rigorous budgeting and clear messaging, startups run out of money earlier than attaining market traction.
- Unsustainable burn charges – Excessive salaries for AI expertise, costly GPU leases and world workplace expansions can drain capital rapidly.
- Funding contraction – World enterprise funding dropped by 42 % between 2022 and 2023, leaving many startups with out observe‑on capital.
- Advertising and communication gaps – A good portion of startup failures stems from insufficient advertising and marketing methods. AI’s complexity makes it exhausting to clarify advantages to prospects.
- Execution and group dynamics – Management misalignment and poor execution account for 18 % and 16 % of failures, respectively.
Professional insights:
- Capital self-discipline – Observe infrastructure and operational prices meticulously. Clarifai’s platform offers utilization analytics to assist groups monitor GPU and API consumption.
- Incremental development – Undertake lean methodologies, launch minimal viable merchandise and iterate rapidly to construct momentum with out overspending.
- Strategic advertising and marketing – Translate technical capabilities into clear worth propositions. Use storytelling, case research and demos focused at particular buyer segments.
- Staff range – Guarantee groups embrace operations specialists, finance professionals and advertising and marketing specialists alongside information scientists.
Aggressive moats and speedy know-how cycles
Fast Abstract
Query: Do AI startups have defensible benefits?
Reply: Aggressive benefits in AI can erode rapidly. In conventional software program, moats could final years, however AI fashions change into out of date when new open‑supply or public fashions are launched. Corporations that construct proprietary fashions with out continuous innovation danger being outcompeted in a single day.
- Speedy commoditization – When a brand new giant mannequin is launched without spending a dime, beforehand defensible fashions change into commodity software program.
- Knowledge moats – Proprietary, area‑particular information can create defensible benefits as a result of information high quality and context are more durable to copy.
- Ecosystem integration – Constructing merchandise that combine deeply into buyer workflows will increase switching prices.
Professional insights:
- Leverage proprietary information – Clarifai allows coaching by yourself information and deploying fashions on a safe platform, serving to create distinctive capabilities.
- Keep adaptable – Repeatedly benchmark fashions and undertake open analysis to maintain tempo with advances.
- Construct platforms, not wrappers – Develop underlying infrastructure and instruments that others construct upon, creating community results.
The shadow AI financial system and inner adoption
Fast Abstract
Query: What’s the shadow AI financial system and the way does it have an effect on startups?
Reply: Whereas enterprise AI pilots battle, a “shadow AI financial system” thrives as workers undertake unsanctioned AI instruments to spice up productiveness. Analysis exhibits that 90 % of workers use private AI instruments at work, usually paying out of pocket. These instruments ship particular person advantages however stay invisible to company management.
- Backside‑up adoption – Workers undertake AI to scale back workload, however these features don’t translate into enterprise transformation as a result of instruments don’t combine with workflows.
- Lack of governance – Shadow AI raises safety and compliance dangers; unsanctioned instruments could expose delicate information.
- Missed studying alternatives – Organizations fail to seize suggestions and studying from shadow utilization, deepening the training hole.
Professional insights:
- Embrace managed experimentation – Encourage workers to experiment with AI instruments inside a governance framework. Clarifai’s platform helps sandbox environments for prototyping and person suggestions.
- Seize insights from shadow utilization – Monitor which duties workers automate and incorporate these workflows into official options.
- Bridge backside‑up and high‑down – Empower line managers to champion AI adoption and combine instruments into processes.
Future‑proof methods and rising traits
Fast Abstract
Query: How can AI startups construct resilience for the long run?
Reply: To outlive in an more and more aggressive panorama, AI startups should undertake price‑environment friendly fashions, strong information governance, moral and regulatory compliance, and sustainable practices. Rising traits—together with small language fashions (SLMs), agentic AI programs, vitality‑conscious compute orchestration, and automated compliance—provide paths ahead.
- Small and specialised fashions – The shift towards Small Language Fashions (SLMs) can scale back compute prices and permit deployment on edge units, enabling offline or personal inference. Sundeep Teki’s evaluation highlights how main organizations are pivoting to extra environment friendly and agile SLMs.
- Agentic AI – Agentic programs can autonomously execute duties inside boundaries, enabling AI to study from suggestions and act, not simply generate.
- Automated compliance – Automated compliance triggers may make rules efficient solely when AI instruments can automate compliance duties. Startups ought to spend money on compliance‑automating AI to scale back regulatory burdens.
- Power‑conscious orchestration – Scheduling compute workloads based mostly on renewable availability and carbon depth reduces prices and environmental impression. Clarifai’s orchestration can incorporate carbon‑conscious methods.
- Knowledge marketplaces and partnerships – Collaborate with information‑wealthy organizations or educational establishments to entry excessive‑high quality information. Pilot exchanges for information rights can scale back the info preparation tax.
- Modular architectures – Construct modular, plug‑and‑play AI elements that may rapidly combine new fashions or information sources.
Professional insights:
- Clarifai’s roadmap – Clarifai continues to spend money on compute effectivity, mannequin compression, information privateness, and regulatory compliance instruments. By utilizing Clarifai, startups can entry a mature AI stack with out heavy infrastructure investments.
- Expertise technique – Rent area specialists who perceive the issue house and pair them with machine‑studying engineers. Encourage steady studying and cross‑disciplinary collaboration.
- Neighborhood engagement – Take part in open‑supply communities and contribute to widespread tooling to remain on the innovative.
Conclusion: Constructing resilient, accountable AI startups
AI’s excessive failure charges stem from misaligned expectations, poor product‑market match, inadequate information readiness, runaway infrastructure prices, dependence on exterior fashions, management missteps, regulatory complexity and useful resource constraints. However failure isn’t inevitable. Profitable startups give attention to fixing actual issues, constructing strong information foundations, managing compute prices, proudly owning their IP, fostering interdisciplinary groups, prioritizing ethics and compliance, and embracing sustainability.
Clarifai’s complete AI platform may also help tackle many of those challenges. Its compute orchestration optimizes GPU utilization and price, mannequin inference instruments allow you to deploy fashions on cloud or edge with ease, and native runner choices guarantee privateness and compliance. With constructed‑in information annotation, mannequin administration, and governance capabilities, Clarifai gives a unified surroundings the place startups can iterate rapidly, preserve regulatory compliance, and scale sustainably.
FAQs
Q1. What proportion of AI startups fail?
Roughly 90 % of AI startups fail inside their first yr, far exceeding the failure charge of conventional tech startups. Furthermore, 95 % of enterprise AI pilots by no means make it to manufacturing.
Q2. Is lack of information the first purpose AI tasks fail?
Lack of information readiness—fairly than sheer quantity—is a high impediment. Over 80 % of AI tasks fail because of poor information high quality and governance. Excessive‑high quality, context‑wealthy information and strong governance frameworks are important.
Q3. How can startups handle AI infrastructure prices?
Startups ought to separate R&D and manufacturing budgets, implement price intelligence to observe per‑request spending, undertake smaller fashions, and negotiate versatile GPU commitments. Utilizing native inference and compute orchestration platforms like Clarifai’s reduces cloud dependence.
This autumn. What position do rules play in AI failure?
Greater than 70 % of IT leaders view regulatory compliance as a high concern. A patchwork of legal guidelines can enhance prices and uncertainty. Early governance frameworks and automatic compliance instruments assist navigate this complexity.
Q5. How does sustainability have an effect on AI startups?
AI workloads eat vital vitality and water. Knowledge centres are projected to make use of 945 TWh by 2030, and AI may account for over 20 % of electrical energy demand development. Power‑conscious compute scheduling and mannequin effectivity are essential for sustainable AI.
Q6. Can small language fashions compete with giant fashions?
Sure. Small language fashions (SLMs) ship a big share of the efficiency of big fashions at a fraction of the associated fee and vitality. Many main organizations are transitioning to SLMs to construct extra environment friendly AI merchandise.