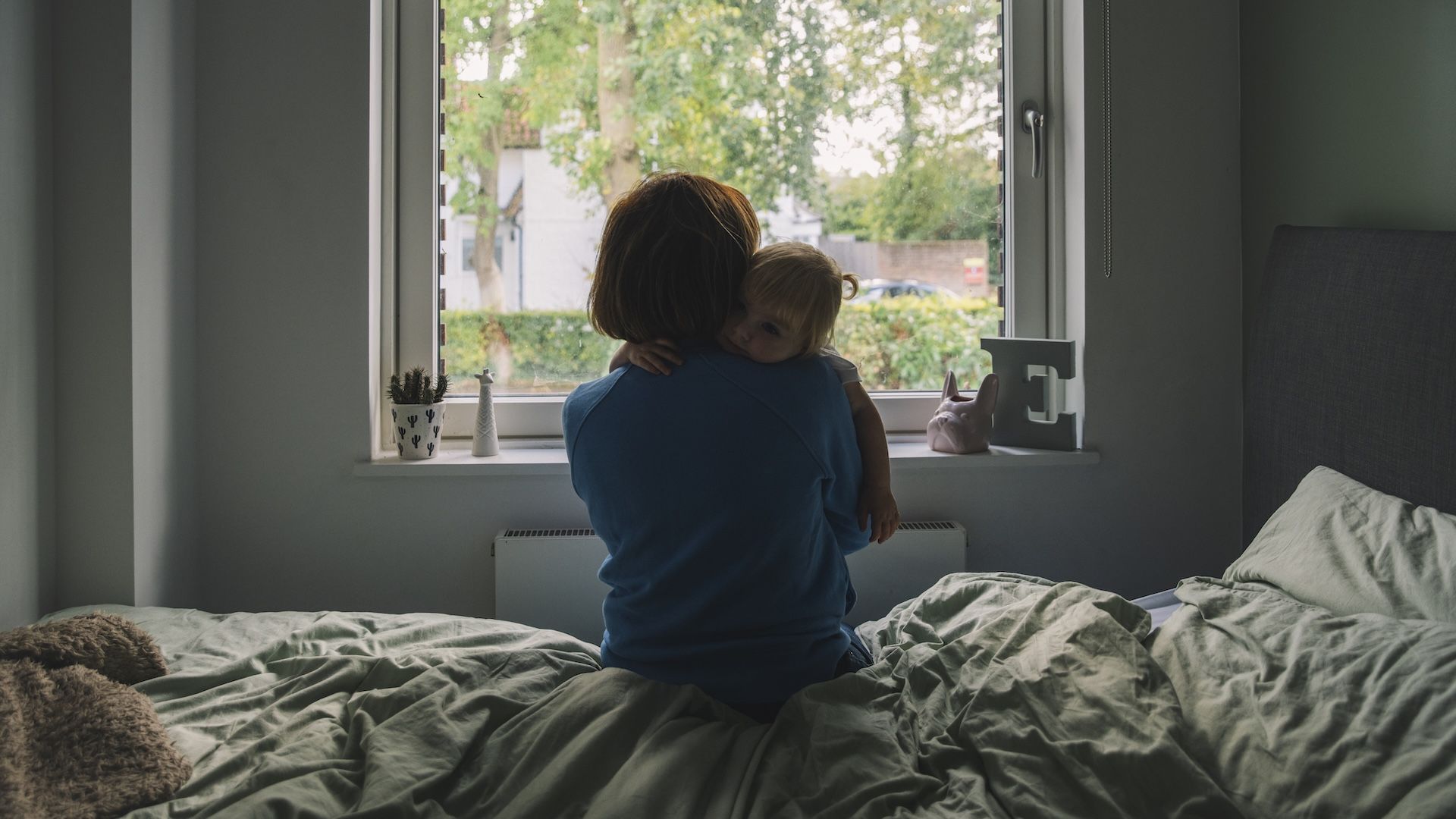
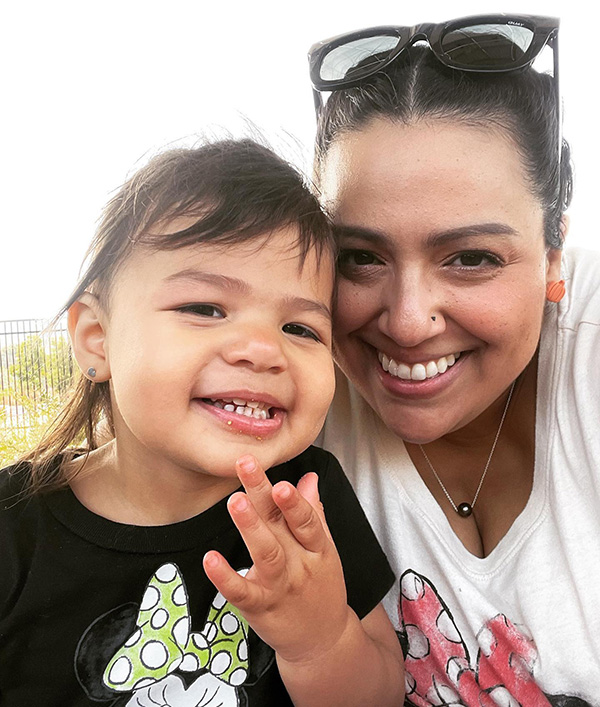
Like many first-time moms, Lisette Lopez-Rose thought childbirth would usher in a time of pleasure. As an alternative, she had panic assaults as she imagined that one thing unhealthy was going to occur to her child, and he or she felt weighed down by a unhappiness that would not elevate. The San Francisco Bay Space mom knew her excessive feelings weren’t regular, however she was afraid to inform her obstetrician. What in the event that they took her child away?
At about six months postpartum, she found an internet community of ladies with related experiences and finally opened as much as her main care physician. “About two months after I began remedy, I began to really feel like I used to be popping out of a deep gap and seeing gentle once more,” she says. As we speak, Lopez-Rose works at Postpartum Help Worldwide, coordinating volunteers to assist new moms type on-line connections.
The primary-ever drug for postpartum melancholy, containing a by-product of progesterone, acquired US Meals and Drug Administration approval in 2019. That marked a brand new method to the dysfunction. This winter, in one other main advance, a San Diego-based startup firm will launch a blood check that predicts a pregnant lady’s danger of postpartum melancholy with greater than 80 % accuracy.
The product, referred to as myLuma, would be the first commercially out there check to make use of biomarkers — molecules within the physique, on this case the blood — to foretell onset of a psychiatric dysfunction, a lot in the way in which that blood checks can detect indicators of illnesses like most cancers and diabetes. Pregnant girls who study they’re in danger for postpartum melancholy might take preventive steps corresponding to taking antidepressants after childbirth or arranging for additional help.
A blood check might scale back the stigma that retains many ladies from looking for assist, says Jennifer Payne, a reproductive psychiatrist on the College of Virginia in Charlottesville and a lead investigator on the research that led to the brand new check. She is a founder and member of the scientific advisory board for the corporate that makes myLuma, Dionysus Well being.
“If we have now a blood check, it brings psychiatry right down to the extent of biology, which I feel your common individual can perceive as one thing that wants remedy and that is not simply in anyone’s head,” she says.
Unpredictable results of hormones
Payne was a fellow on the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being in 2001 when she grew to become intrigued by postpartum melancholy as a window into the onset of temper problems. That led her to a key query: Why does the sudden drop in hormones after childbirth vastly have an effect on some girls however not others? Whereas it isn’t unusual for ladies to expertise transient emotions of hysteria and unhappiness inside days of giving beginning, solely in some does a deeper and extra persistent melancholy take maintain.

As Payne’s analysis advanced, she teamed up with Zachary Kaminsky, then a colleague at Johns Hopkins College, who studied the consequences of estrogen on mouse brains. Kaminsky is an epigeneticist: He researches how small chemical compounds referred to as methyl teams can connect to genes and have an effect on how lively they’re. Environmental elements from air pollution to vitamin can have an effect on the extent of this reversible methylation.
By evaluating feminine mice given excessive ranges of estrogen to these with out it, Kaminsky discovered that estrogen precipitated particular gene methylation patterns inside cells within the hippocampus, part of the mind that helps management temper. These findings steered what to search for in blood samples Payne had collected from 51 girls with a historical past of temper problems. The ladies had been tracked all through their pregnancies and afterward, with some creating postpartum melancholy inside 4 weeks of childbirth.
Two estrogen-sensitive genes emerged from the analysis — HP1BP3 and TTC9B. Greater than 80 % of the ladies who had postpartum melancholy confirmed a particular sample of larger methylation on one gene and fewer methylation on the opposite. What’s extra, the adjustments within the genes may very well be detected all through every trimester of being pregnant, says Kaminsky, now on the College of Ottawa Institute of Psychological Well being Analysis on the Royal; he is also a cofounder of Dionysus. In different phrases, even early in being pregnant, Kaminsky says, “you possibly can predict the ladies which are going to get postpartum melancholy.”
Kaminsky, Payne and collaborators repeatedly replicated these findings. As reported in a 2016 paper in Neuropharmacology, they discovered that by the methylation patterns of these genes, they might appropriately predict greater than 80 % of the instances of postpartum melancholy in 240 pregnant girls who had no historical past of psychiatric problems. In one other collaboration printed in 2020 in Psychiatry Analysis, scientists at Johns Hopkins, Emory College and the College of California, Irvine, together with Payne and Kaminsky, examined blood samples from 285 pregnant girls and likewise confirmed the findings.
That epigenetic analysis kinds the premise of the myLuma check, which additionally incorporates extra biomarkers that enhance its accuracy, says Kaminsky. Starting in January 2026, it’s anticipated to turn out to be out there at some medical doctors’ workplaces in three states: Florida, Texas and California. Although it is not but FDA-approved, medical doctors are permitted to make use of such lab checks to assist make scientific selections.
Zeroing in on steroids
Not everybody with postpartum melancholy has these epigenetic adjustments, so Payne and different researchers proceed to hunt for different biomarkers to grasp how hormonal adjustments set off postpartum melancholy. They’re zeroing in, for instance, on neuroactive steroids, which the physique makes from molecules like progesterone within the mind and different tissues.
A kind of metabolites, referred to as allopregnanolone, has a chilled impact — it impacts a receptor within the mind referred to as GABA-A, which is thought to be concerned in stress discount. Allopregnanolone rises throughout being pregnant and drops swiftly after supply. One other neuroactive steroid, pregnanolone, has related properties. A 3rd, isoallopregnanolone, tamps down the antidepressant impact of allopregnanolone, growing emotions of stress.
In a research of 136 pregnant girls printed in 2025 within the journal Neuropsychopharmacology, girls with an imbalance in pregnanolone and isoallopregnanolone throughout being pregnant have been extra more likely to develop postpartum melancholy. Measuring the ratio of those chemical compounds within the blood may very well be one other option to predict postpartum melancholy, says reproductive psychiatrist Lauren M. Osborne of Weill Cornell Drugs in New York Metropolis, who co-led the research with Payne.
Allopregnanolone, in the meantime, has already proved to be a helpful device for remedy. An artificial model referred to as brexanolone was developed by Cambridge, Massachusetts-based Sage Therapeutics and FDA-approved in 2019 — the primary drug accredited particularly for postpartum melancholy. Initially offered by way of IV infusion, it has been changed by an oral model, zuranolone, which was FDA-approved in 2023.
If we have now a blood check, it brings psychiatry right down to the extent of biology, which I feel your common individual can perceive as one thing that wants remedy and that isn’t simply in anyone’s head.
Jennifer Payne, College of Virginia in Charlottesville
These are “transformative therapies” as a result of they work quickly, write the authors of a 2025 article within the Annual Evaluate of Drugs. Ladies at excessive danger of postpartum melancholy would possibly even profit from proactively taking zuranolone, although that hasn’t but been examined, says article coauthor Samantha Meltzer-Brody, a reproductive psychiatrist on the College of North Carolina who was a tutorial principal investigator in research of brexanolone and an investigator in zuranolone trials.
The supply of a blood check, she provides, “opens up that whole line of questioning on how do you get forward of it, so you do not have to attend till somebody begins struggling?”
There are different doable targets for a postpartum melancholy check. In a 2022 article in Molecular Psychiatry, Johns Hopkins neuroscientist Sarven Sabunciyan, with Osborne, Payne and Morgan Sherer, then an immunologist at Johns Hopkins, described a small research through which the sorts of RNA carried by blood in fatty bubbles have been totally different in girls who developed postpartum melancholy — each in being pregnant and afterwards. Specifically, there was a lower in sorts of RNA associated to autophagy — the cleaning of particles from cells. Autophagy has been linked to different psychiatric problems.
In one other potential lead, Eynav Accortt, a scientific psychologist specializing in perinatal psychological well being at Cedars-Sinai Medical Heart in Los Angeles, discovered a sample of altered proteins in plasma samples of ladies who developed perinatal temper and anxiousness problems, a bunch of situations that features postpartum melancholy. This included proteins concerned in neuron perform and in irritation, which is thought to play a task in melancholy.
As researchers proceed to discover these prospects, Payne is main a big scientific trial that may present extra detailed data on the predictive worth of the myLuma check. For instance, it is going to discover the charges of false positives (girls who’re recognized as at-risk who don’t develop postpartum melancholy) and false negatives (girls who develop postpartum melancholy however weren’t recognized by the check). That could be a needed step towards FDA approval, which might make the check out there on to pregnant girls.
Lopez-Rose remembers how scared she felt within the months after her daughter was born. In these darkish occasions, she give up her job, barely slept and was overwhelmed by unfavourable ideas. She had many self-doubts, however she now is aware of that reaching out for assist was an indication that she was a superb mom.
As we speak, her daughter is 4 — and thriving, as is Lopez-Rose. However a blood check, she says, would have warned her of what to look out for, “as an alternative of it being so stunning once I was going by my melancholy.”
This text initially appeared in Knowable Journal, a nonprofit publication devoted to creating scientific information accessible to all. Join Knowable Journal’s publication.