Picture by Creator
# The Setup
You are about to coach a mannequin whenever you discover 20% of your values are lacking. Do you drop these rows? Fill them in with averages? Use one thing fancier? The reply issues greater than you’d suppose.
Should you Google it, you will discover dozens of imputation strategies, from the dead-simple (simply use the imply) to the delicate (iterative machine studying fashions). You would possibly suppose that fancy strategies are higher. KNN considers related rows. MICE builds predictive fashions. They have to outperform simply slapping on the typical, proper?
We thought so too. We have been fallacious.
# The Experiment
We grabbed the Crop Advice dataset from StrataScratch initiatives – 2,200 soil samples throughout 22 crop varieties, with options akin to nitrogen ranges, temperature, humidity, and rainfall. A Random Forest hits 99.6% accuracy on this factor. It is nearly suspiciously clear.
This evaluation extends our Agricultural Knowledge Evaluation challenge, which explores the identical dataset via EDA and statistical testing. Right here, we ask: what occurs when clear knowledge meets a real-world drawback – lacking values?
Excellent for our experiment.
We launched 20% lacking values (fully at random, simulating sensor failures), then examined 5 imputation strategies:


Our testing was thorough; we used 10-fold cross-validation throughout 5 random seeds (a complete of fifty runs per methodology). To make sure that no info from the check set leaked into the coaching set, our imputation fashions have been educated on the coaching units solely. For our statistical checks, we utilized the Bonferroni correction. We additionally normalized the enter options for each KNN and MICE, as if we didn’t normalize them, an enter with values ranging between 0 and 300 (rainfall) would have a a lot larger impression than an enter with a spread of three to 10 (pH) when performing the space calculation for these strategies. Full code and reproducible outcomes can be found in our pocket book.
Then we ran it and stared on the outcomes.
# The Shock
Here is what we anticipated: KNN or MICE would win, as a result of they’re smarter. They think about relationships between options. They use precise machine studying.
Here is what we received:


The Median and Imply are tied for first place. The delicate strategies got here in third and fourth.
We ran the statistical check. Imply vs. Median: p = 0.7. Not even near vital. They’re successfully equivalent.
However this is the kicker: each of them considerably outperformed KNN and MICE (p < 0.001 after Bonferroni correction). The easy strategies did not simply match the flowery ones. They beat them.
# Wait, What?
Earlier than you throw out your MICE set up, let’s dig into why this occurred.
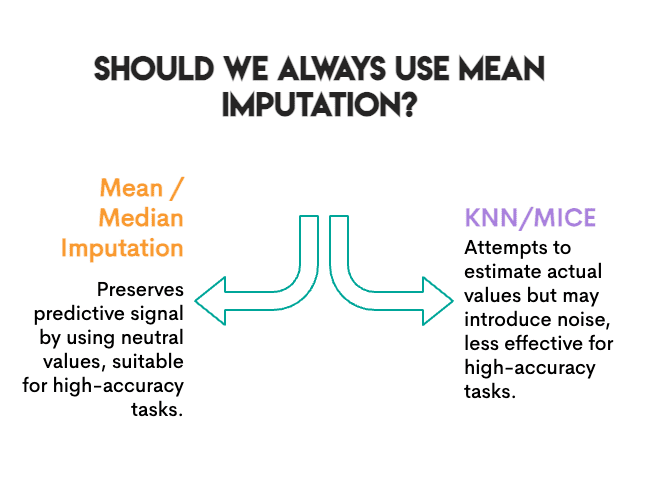
The duty was prediction. We measured accuracy. Does the mannequin nonetheless classify crops appropriately after imputation? For that particular aim, what issues is preserving the predictive sign, not essentially the precise values.
Imply imputation does one thing attention-grabbing: it replaces lacking values with a “impartial” worth that does not push the mannequin towards any explicit class. It is boring, but it surely’s protected. The Random Forest can nonetheless discover its determination boundaries.
KNN and MICE strive tougher; they estimate what the precise worth may need been. However in doing so, they’ll introduce noise. If the closest neighbors aren’t that related, or if MICE’s iterative modeling picks up spurious patterns, you is likely to be including error slightly than eradicating it.
The baseline was already excessive. At 99.6% accuracy, it is a fairly simple classification drawback. When the sign is powerful, imputation errors matter much less. The mannequin can afford some noise.
Random Forest is powerful. Tree-based fashions deal with imperfect knowledge properly. A linear mannequin struggled extra with the variance distortion of imply imputation.

Not so quick.
# The Plot Twist
We measured one thing else: correlation preservation.
Here is the factor about actual knowledge: options do not exist in isolation. They transfer collectively. In our dataset, when soil has excessive Phosphorus, it normally has excessive Potassium as properly (correlation of 0.74). This is not random; farmers sometimes add these vitamins collectively, and sure soil varieties retain each equally.
If you impute lacking values, chances are you’ll by chance break these relationships. Imply imputation fills in “common Potassium” no matter what Phosphorus seems to be like in that row. Try this sufficient occasions, and the connection between P and Okay begins to fade. Your imputed knowledge would possibly look fantastic column-by-column, however the relationships between columns are quietly falling aside.
Why does this matter? If the next step is clustering, PCA, or any evaluation the place characteristic relationships are the purpose, you are working with broken knowledge and do not even understand it.
We checked: after imputation, how a lot of that P↔Okay correlation survived?


Picture by Creator
The rankings fully flipped.
KNN preserved the correlation nearly completely. Imply and Median destroyed a couple of quarter of it. And Random Pattern (which samples values independently for every column) eradicated the connection.
This is sensible. Imply imputation replaces lacking values with the identical quantity no matter what the opposite options appear like. If a row has excessive Nitrogen, Imply does not care; it nonetheless imputes the typical Potassium. KNN seems to be at related rows, so if high-N rows are inclined to have high-Okay, it will impute a high-Okay worth.
# The Commerce-Off
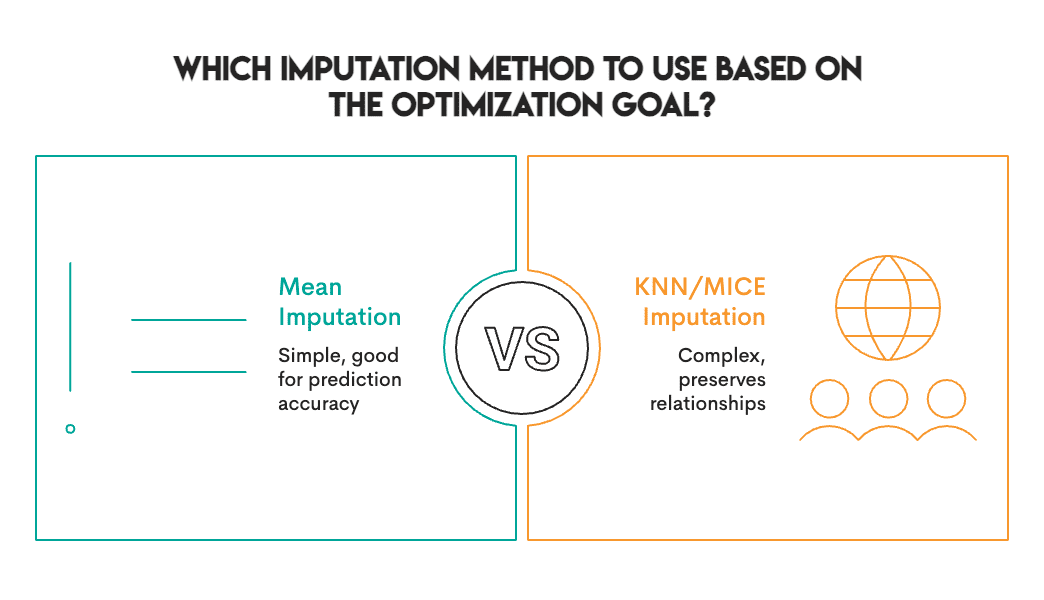
Here is the actual discovering: there isn’t a single finest imputation methodology. As a substitute, choose essentially the most acceptable methodology primarily based in your particular aim and context.
The accuracy rankings and correlation rankings are almost reverse:


Picture by Creator
(A minimum of the Random Pattern is constant – it is dangerous at all the pieces.)
This trade-off is not distinctive to our dataset. It is baked into how these strategies work. Imply/Median are univariate, and so they have a look at one column at a time. KNN/MICE are multivariate, and so they think about relationships. Univariate strategies protect marginal distributions however destroy correlation. Multivariate strategies protect construction and may produce some type of predictive error/noise.
# So, What Ought to You Truly Do?
After operating this experiment and digging via the literature, this is our sensible information:
Use Imply or Median when:
- Your aim is prediction (classification, regression)
- You are utilizing a sturdy mannequin (Random Forest, XGBoost, neural nets)
- Lacking fee is below 30%
- You want one thing quick
Use KNN when:
- You have to protect characteristic relationships
- Downstream job is clustering, PCA, or visualization
- You need correlations to outlive for exploratory evaluation
Use MICE when:
- You want legitimate customary errors (for statistical inference)
- You are reporting confidence intervals or p-values
- The lacking knowledge mechanism is likely to be MAR (Lacking at Random)
Keep away from Random Pattern:
- It is tempting as a result of it “preserves the distribution”
- Nevertheless it destroys all multivariate construction
- We could not discover a good use case
# The Trustworthy Caveats
We examined one dataset, one lacking fee (20%), one mechanism (MCAR), and one downstream mannequin (Random Forest). Your setup might differ. The literature exhibits that on different datasets, MissForest and MICE usually carry out higher. Our discovering that straightforward strategies compete is actual, but it surely’s not common.
# The Backside Line
We went into this experiment anticipating to verify that refined imputation strategies are definitely worth the complexity. As a substitute, we discovered that for prediction accuracy, the standard imply held its personal, whereas fully failing at preserving the relationships between options.
The lesson is not “at all times use imply imputation.” It is “know what you are optimizing for.”

Picture by Creator
Should you simply want predictions, begin easy. Take a look at whether or not KNN or MICE truly helps in your knowledge. Do not assume they may.
Should you want the correlation construction for downstream evaluation, Imply will silently wreck it whereas providing you with completely affordable accuracy numbers. That is a lure.
And no matter you do, scale your options earlier than utilizing KNN. Belief us on this one.
Nate Rosidi is an information scientist and in product technique. He is additionally an adjunct professor educating analytics, and is the founding father of StrataScratch, a platform serving to knowledge scientists put together for his or her interviews with actual interview questions from high firms. Nate writes on the most recent traits within the profession market, provides interview recommendation, shares knowledge science initiatives, and covers all the pieces SQL.

