Manufacturing LLM serving is now a techniques drawback, not a generate() loop. For actual workloads, the selection of inference stack drives your tokens per second, tail latency, and finally value per million tokens on a given GPU fleet.
This comparability focuses on 4 broadly used stacks:
- vLLM
- NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM
- Hugging Face Textual content Technology Inference (TGI v3)
- LMDeploy
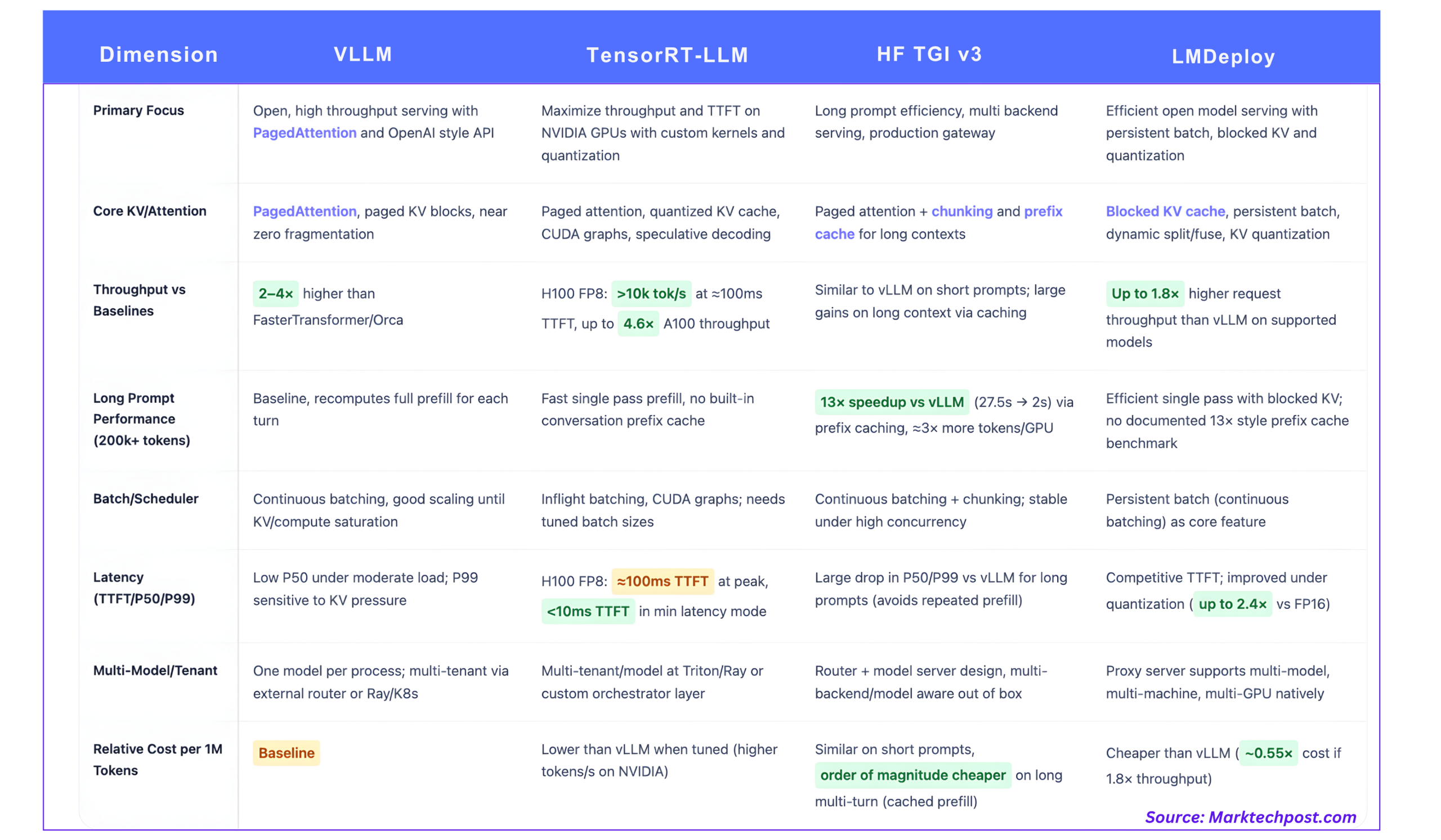
1. vLLM, PagedAttention because the open baseline
Core thought
vLLM is constructed round PagedAttention, an consideration implementation that treats the KV cache like paged digital reminiscence somewhat than a single contiguous buffer per sequence.
As a substitute of allocating one huge KV area per request, vLLM:
- Divides KV cache into fastened measurement blocks
- Maintains a block desk that maps logical tokens to bodily blocks
- Shares blocks between sequences wherever prefixes overlap
This reduces exterior fragmentation and lets the scheduler pack many extra concurrent sequences into the identical VRAM.
Throughput and latency
vLLM improves throughput by 2–4× over techniques like FasterTransformer and Orca at comparable latency, with bigger beneficial properties for longer sequences.
Key properties for operators:
- Steady batching (additionally known as inflight batching) merges incoming requests into current GPU batches as a substitute of ready for fastened batch home windows.
- On typical chat workloads, throughput scales near linearly with concurrency till KV reminiscence or compute saturates.
- P50 latency stays low for average concurrency, however P99 can degrade as soon as queues are lengthy or KV reminiscence is tight, particularly for prefill heavy queries.
vLLM exposes an OpenAI appropriate HTTP API and integrates nicely with Ray Serve and different orchestrators, which is why it’s broadly used as an open baseline.
KV and multi tenant
- PagedAttention offers close to zero KV waste and versatile prefix sharing inside and throughout requests.
- Every vLLM course of serves one mannequin, multi tenant and multi mannequin setups are often constructed with an exterior router or API gateway that followers out to a number of vLLM cases.
2. TensorRT-LLM, {hardware} most on NVIDIA GPUs
Core thought
TensorRT-LLM is NVIDIA’s optimized inference library for his or her GPUs. The library supplies customized consideration kernels, inflight batching, paged KV caching, quantization all the way down to FP4 and INT4, and speculative decoding.
It’s tightly coupled to NVIDIA {hardware}, together with FP8 tensor cores on Hopper and Blackwell.
Measured efficiency
NVIDIA’s H100 vs A100 analysis is probably the most concrete public reference:
- On H100 with FP8, TensorRT-LLM reaches over 10,000 output tokens/s at peak throughput for 64 concurrent requests, with ~100 ms time to first token.
- H100 FP8 achieves as much as 4.6× larger max throughput and 4.4× quicker first token latency than A100 on the identical fashions.
For latency delicate modes:
- TensorRT-LLM on H100 can drive TTFT beneath 10 ms in batch 1 configurations, at the price of decrease total throughput.
These numbers are mannequin and form particular, however they provide a practical scale.
Prefill vs decode
TensorRT-LLM optimizes each phases:
- Prefill advantages from excessive throughput FP8 consideration kernels and tensor parallelism
- Decode advantages from CUDA graphs, speculative decoding, quantized weights and KV, and kernel fusion
The consequence may be very excessive tokens/s throughout a variety of enter and output lengths, particularly when the engine is tuned for that mannequin and batch profile.
KV and multi tenant
TensorRT-LLM supplies:
- Paged KV cache with configurable structure
- Assist for lengthy sequences, KV reuse and offloading
- Inflight batching and precedence conscious scheduling primitives
NVIDIA pairs this with Ray primarily based or Triton primarily based orchestration patterns for multi tenant clusters. Multi mannequin help is completed on the orchestrator stage, not inside a single TensorRT-LLM engine occasion.
3. Hugging Face TGI v3, lengthy immediate specialist and multi backend gateway
Core thought
Textual content Technology Inference (TGI) is a Rust and Python primarily based serving stack that provides:
- HTTP and gRPC APIs
- Steady batching scheduler
- Observability and autoscaling hooks
- Pluggable backends, together with vLLM type engines, TensorRT-LLM, and different runtimes
Model 3 focuses on lengthy immediate processing by means of chunking and prefix caching.
Lengthy immediate benchmark vs vLLM
The TGI v3 docs give a transparent benchmark:
- On lengthy prompts with greater than 200,000 tokens, a dialog reply that takes 27.5 s in vLLM could be served in about 2 s in TGI v3.
- That is reported as a 13× speedup on that workload.
- TGI v3 is ready to course of about 3× extra tokens in the identical GPU reminiscence by decreasing its reminiscence footprint and exploiting chunking and caching.
The mechanism is:
- TGI retains the unique dialog context in a prefix cache, so subsequent turns solely pay for incremental tokens
- Cache lookup overhead is on the order of microseconds, negligible relative to prefill compute
This can be a focused optimization for workloads the place prompts are extraordinarily lengthy and reused throughout turns, for instance RAG pipelines and analytic summarization.
Structure and latency conduct
Key elements:
- Chunking, very lengthy prompts are cut up into manageable segments for KV and scheduling
- Prefix caching, knowledge construction to share lengthy context throughout turns
- Steady batching, incoming requests be part of batches of already working sequences
- PagedAttention and fused kernels within the GPU backends
For brief chat type workloads, throughput and latency are in the identical ballpark as vLLM. For lengthy, cacheable contexts, each P50 and P99 latency enhance by an order of magnitude as a result of the engine avoids repeated prefill.
Multi backend and multi mannequin
TGI is designed as a router plus mannequin server structure. It may possibly:
- Route requests throughout many fashions and replicas
- Goal totally different backends, for instance TensorRT-LLM on H100 plus CPU or smaller GPUs for low precedence visitors
This makes it appropriate as a central serving tier in multi tenant environments.
4. LMDeploy, TurboMind with blocked KV and aggressive quantization
Core thought
LMDeploy from the InternLM ecosystem is a toolkit for compressing and serving LLMs, centered across the TurboMind engine. It focuses on:
- Excessive throughput request serving
- Blocked KV cache
- Persistent batching (steady batching)
- Quantization of weights and KV cache
Relative throughput vs vLLM
The challenge states:
- ‘LMDeploy delivers as much as 1.8× larger request throughput than vLLM‘, with the help from persistent batch, blocked KV, dynamic cut up and fuse, tensor parallelism and optimized CUDA kernels.
KV, quantization and latency
LMDeploy consists of:
- Blocked KV cache, much like paged KV, that helps pack many sequences into VRAM
- Assist for KV cache quantization, sometimes int8 or int4, to chop KV reminiscence and bandwidth
- Weight solely quantization paths equivalent to 4 bit AWQ
- A benchmarking harness that experiences token throughput, request throughput, and first token latency
This makes LMDeploy engaging while you wish to run bigger open fashions like InternLM or Qwen on mid vary GPUs with aggressive compression whereas nonetheless sustaining good tokens/s.
Multi mannequin deployments
LMDeploy supplies a proxy server in a position to deal with:
- Multi mannequin deployments
- Multi machine, multi GPU setups
- Routing logic to pick fashions primarily based on request metadata
So architecturally it sits nearer to TGI than to a single engine.
What to make use of when?
- If you need most throughput and really low TTFT on NVIDIA GPUs
- TensorRT-LLM is the first alternative
- It makes use of FP8 and decrease precision, customized kernels and speculative decoding to push tokens/s and hold TTFT beneath 100 ms at excessive concurrency and beneath 10 ms at low concurrency
- In case you are dominated by lengthy prompts with reuse, equivalent to RAG over massive contexts
- TGI v3 is a robust default
- Its prefix cache and chunking give as much as 3× token capability and 13× decrease latency than vLLM in printed lengthy immediate benchmarks, with out additional configuration
- If you need an open, easy engine with robust baseline efficiency and an OpenAI type API
- vLLM stays the usual baseline
- PagedAttention and steady batching make it 2–4× quicker than older stacks at comparable latency, and it integrates cleanly with Ray and K8s
- Should you goal open fashions equivalent to InternLM or Qwen and worth aggressive quantization with multi mannequin serving
- LMDeploy is an effective match
- Blocked KV cache, persistent batching and int8 or int4 KV quantization give as much as 1.8× larger request throughput than vLLM on supported fashions, with a router layer included
In follow, many dev groups combine these techniques, for instance utilizing TensorRT-LLM for prime quantity proprietary chat, TGI v3 for lengthy context analytics, vLLM or LMDeploy for experimental and open mannequin workloads. The bottom line is to align throughput, latency tails, and KV conduct with the precise token distributions in your visitors, then compute value per million tokens from measured tokens/s by yourself {hardware}.
References
- vLLM / PagedAttention
- TensorRT-LLM efficiency and overview
- HF Textual content Technology Inference (TGI v3) long-prompt conduct
- LMDeploy / TurboMind


