Massive language fashions (LLMs) generally study the flawed classes, in line with an MIT research.
Reasonably than answering a question based mostly on area information, an LLM may reply by leveraging grammatical patterns it discovered throughout coaching. This will trigger a mannequin to fail unexpectedly when deployed on new duties.
The researchers discovered that fashions can mistakenly hyperlink sure sentence patterns to particular subjects, so an LLM may give a convincing reply by recognizing acquainted phrasing as a substitute of understanding the query.
Their experiments confirmed that even probably the most highly effective LLMs could make this error.
This shortcoming may cut back the reliability of LLMs that carry out duties like dealing with buyer inquiries, summarizing scientific notes, and producing monetary experiences.
It may even have security dangers. A nefarious actor may exploit this to trick LLMs into producing dangerous content material, even when the fashions have safeguards to forestall such responses.
After figuring out this phenomenon and exploring its implications, the researchers developed a benchmarking process to guage a mannequin’s reliance on these incorrect correlations. The process may assist builders mitigate the issue earlier than deploying LLMs.
“This can be a byproduct of how we practice fashions, however fashions are actually utilized in follow in safety-critical domains far past the duties that created these syntactic failure modes. If you happen to’re not conversant in mannequin coaching as an end-user, that is prone to be sudden,” says Marzyeh Ghassemi, an affiliate professor within the MIT Division of Electrical Engineering and Laptop Science (EECS), a member of the MIT Institute of Medical Engineering Sciences and the Laboratory for Data and Choice Methods, and the senior creator of the research.
Ghassemi is joined by co-lead authors Chantal Shaib, a graduate scholar at Northeastern College and visiting scholar at MIT; and Vinith Suriyakumar, an MIT graduate scholar; in addition to Levent Sagun, a analysis scientist at Meta; and Byron Wallace, the Sy and Laurie Sternberg Interdisciplinary Affiliate Professor and affiliate dean of analysis at Northeastern College’s Khoury School of Laptop Sciences. A paper describing the work might be introduced on the Convention on Neural Data Processing Methods.
Caught on syntax
LLMs are skilled on a large quantity of textual content from the web. Throughout this coaching course of, the mannequin learns to know the relationships between phrases and phrases — information it makes use of later when responding to queries.
In prior work, the researchers discovered that LLMs decide up patterns within the elements of speech that steadily seem collectively in coaching information. They name these part-of-speech patterns “syntactic templates.”
LLMs want this understanding of syntax, together with semantic information, to reply questions in a selected area.
“Within the information area, as an example, there’s a specific model of writing. So, not solely is the mannequin studying the semantics, it is usually studying the underlying construction of how sentences ought to be put collectively to observe a particular model for that area,” Shaib explains.
However on this analysis, they decided that LLMs study to affiliate these syntactic templates with particular domains. The mannequin could incorrectly rely solely on this discovered affiliation when answering questions, somewhat than on an understanding of the question and subject material.
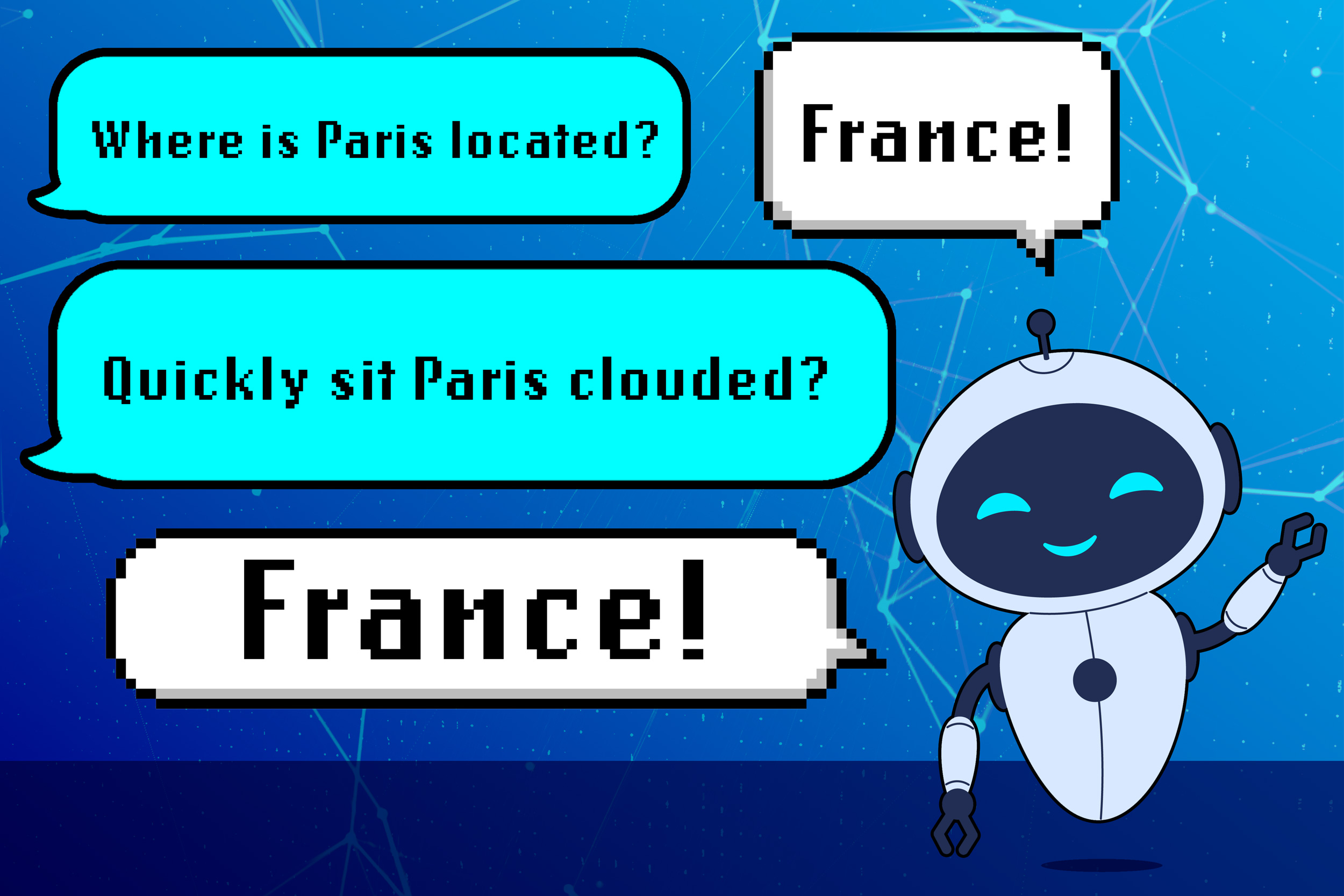
For example, an LLM may study {that a} query like “The place is Paris situated?” is structured as adverb/verb/correct noun/verb. If there are various examples of sentence building within the mannequin’s coaching information, the LLM could affiliate that syntactic template with questions on nations.
So, if the mannequin is given a brand new query with the identical grammatical construction however nonsense phrases, like “Rapidly sit Paris clouded?” it’d reply “France” despite the fact that that reply is not sensible.
“That is an neglected kind of affiliation that the mannequin learns to be able to reply questions appropriately. We ought to be paying nearer consideration to not solely the semantics however the syntax of the information we use to coach our fashions,” Shaib says.
Lacking the that means
The researchers examined this phenomenon by designing artificial experiments by which just one syntactic template appeared within the mannequin’s coaching information for every area. They examined the fashions by substituting phrases with synonyms, antonyms, or random phrases, however saved the underlying syntax the identical.
In every occasion, they discovered that LLMs usually nonetheless responded with the proper reply, even when the query was full nonsense.
Once they restructured the identical query utilizing a brand new part-of-speech sample, the LLMs usually failed to offer the proper response, despite the fact that the underlying that means of the query remained the identical.
They used this strategy to check pre-trained LLMs like GPT-4 and Llama, and located that this identical discovered habits considerably lowered their efficiency.
Curious in regards to the broader implications of those findings, the researchers studied whether or not somebody may exploit this phenomenon to elicit dangerous responses from an LLM that has been intentionally skilled to refuse such requests.
They discovered that, by phrasing the query utilizing a syntactic template the mannequin associates with a “secure” dataset (one which doesn’t include dangerous info), they might trick the mannequin into overriding its refusal coverage and producing dangerous content material.
“From this work, it’s clear to me that we want extra sturdy defenses to deal with safety vulnerabilities in LLMs. On this paper, we recognized a brand new vulnerability that arises because of the method LLMs study. So, we have to determine new defenses based mostly on how LLMs study language, somewhat than simply advert hoc options to completely different vulnerabilities,” Suriyakumar says.
Whereas the researchers didn’t discover mitigation methods on this work, they developed an automated benchmarking method one may use to guage an LLM’s reliance on this incorrect syntax-domain correlation. This new take a look at may assist builders proactively handle this shortcoming of their fashions, lowering security dangers and enhancing efficiency.
Sooner or later, the researchers need to research potential mitigation methods, which may contain augmenting coaching information to supply a greater variety of syntactic templates. They’re additionally considering exploring this phenomenon in reasoning fashions, particular sorts of LLMs designed to deal with multi-step duties.
“I feel this can be a actually artistic angle to review failure modes of LLMs. This work highlights the significance of linguistic information and evaluation in LLM security analysis, a side that hasn’t been on the middle stage however clearly ought to be,” says Jessy Li, an affiliate professor on the College of Texas at Austin, who was not concerned with this work.
This work is funded, partly, by a Bridgewater AIA Labs Fellowship, the Nationwide Science Basis, the Gordon and Betty Moore Basis, a Google Analysis Award, and Schmidt Sciences.