- Could 5, 2014
- Vasilis Vryniotis
- . 3 Feedback
Within the ISO analysis undertaking for my MSc in Machine Studying at Imperial Faculty London, I targeted on the issue of Cluster Evaluation through the use of Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions. The DPMMs is a “fully-Bayesian” unsupervised studying approach which not like different Cluster Evaluation strategies doesn’t require us to predefine the full variety of clusters inside our information. Giant corporations, reminiscent of Google, use these infinite Dirichlet combination fashions in a wide range of purposes together with Doc Classification, Pure Language Processing, Laptop Imaginative and prescient and extra.
Replace: The Datumbox Machine Studying Framework is now open-source and free to obtain. Try the bundle com.datumbox.framework.machinelearning.clustering to see the implementation of Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions in Java.
Throughout my analysis I had the chance to work with two totally different combination fashions: the Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin which is used for clustering steady Gaussian datasets and the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin which is used for clustering Paperwork. The unique analysis lasted for 3 months and was carried out below the supervision of Professor Aldo Faisal from Imperial Faculty London. My plan is inside the subsequent weeks to publish an tailored model of my analysis on this weblog, focus on the idea and purposes of Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions and publish a Java implementation which can be utilized to carry out clustering with DPMMs.
This text is the introduction/overview of the analysis, describes the issues, discusses briefly the Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions and at last presents the construction of the upcoming articles.
1. Overview of Cluster Evaluation strategies
Cluster Evaluation is an unsupervised studying approach which targets in figuring out the teams inside a dataset. The teams are chosen in such a approach in order that the observations assigned to them are extra comparable to one another than to the observations which belong to totally different teams. Clustering is an unsupervised approach as a result of it doesn’t make use of annotated datasets with a purpose to estimate the aforementioned clusters. As a substitute the clusters are recognized solely through the use of the traits/options of the information.
The duty of cluster evaluation isn’t linked on to a selected algorithm however fairly there are a number of totally different approaches to mannequin the information. Within the literature we will discover centroid fashions (such because the Okay-means and the Okay-representative) which symbolize the teams as imply vectors, distribution fashions (such because the Combination of Gaussians) which mannequin the generative distributions of the information through the use of statistics and possibilities, Graph Clustering fashions (such because the MCL) which arrange datasets on the premise of the sting construction of the observations, Connectivity fashions (such because the Agglomerative and Divisive algorithms) which deal with the gap connectivity and extra.
Cluster Evaluation algorithms will be additional separated in numerous classes relying on the best way that they arrange the clusters. For instance algorithms can divided primarily based on whether or not they carry out laborious or comfortable clustering (assigning the information factors to a single cluster or to many clusters with a sure chance/weight) and on whether or not they carry out flat, hierarchical or overlapping clustering (whether or not protect a hierarchy within the recognized clusters).
Lastly given the truth that Cluster Evaluation is among the hottest and frequently used Machine Studying strategies, a number of totally different algorithms and fashions have been proposed within the literature. Normally the approach that’s utilized in every case closely depends upon the issue and the kind of information that we now have.
2. Purposes of Clustering
On account of the truth that Cluster Evaluation doesn’t require having annotated datasets that are often costly and tough to seek out, it has turn out to be a robust instrument in many various areas of science and enterprise. Consequently Clustering has quite a few purposes in a lot of totally different fields.
In pc imaginative and prescient clustering is incessantly utilized in picture segmentation and in grouping collectively totally different objects inside a scene. In bioinformatics and neuroscience it may be used to group collectively genes or neurons which are related to specific duties/behaviors. In advertising and marketing and enterprise clustering it’s frequently used to determine teams inside buyer databases and allow corporations to supply extra focused providers. Search engines like google and yahoo use clustering with a purpose to determine comparable paperwork inside their indexes and arrange webpages in classes. Social Networks use clustering to determine communities and cliques inside massive teams of customers. Lastly we should always word that Cluster Evaluation has been efficiently utilized in a number of different areas such Medication, Laptop science, Finance, Social Sciences, Robotics, Physics and extra.
3. The issue of figuring out the variety of Clusters
Probably the most tough issues in clustering is figuring out the full variety of clusters that exist inside the information. Normally most of the current algorithms require the full variety of clusters okay as a parameter earlier than performing the evaluation and their outcomes closely rely upon this parameter. When the variety of clusters okay is thought earlier than hand, then the aforementioned algorithms are capable of present us with the required cluster assignments. However this quantity is never recognized in real-world purposes. Moreover in lots of purposes the variety of clusters is predicted to vary as we add extra observations over time.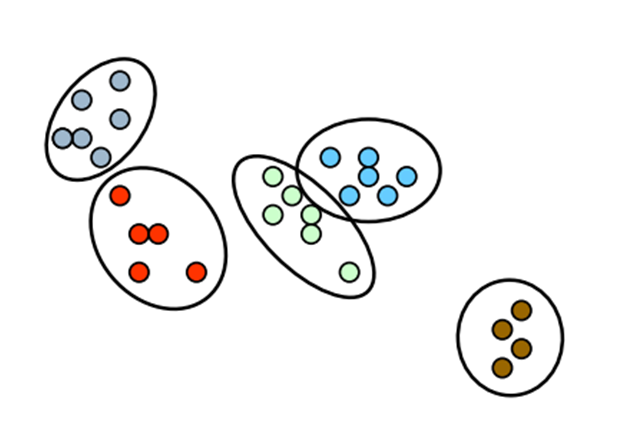
Though a number of strategies have been proposed to keep away from specifying straight the variety of clusters (Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering) or to estimate the optimum variety of clusters from information (reminiscent of X-means), many of the strategies relay heuristics they usually don’t use the probabilistic framework. One different strategy which permits us to estimate dynamically the variety of clusters and adapt it as extra information are noticed is to make use of Dirichlet Processes Combination Fashions.
4. Overview of Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions
The Dirichlet course of is a household of non-parametric Bayesian fashions that are generally used for density estimation, semi-parametric modelling and mannequin choice/averaging. The Dirichlet processes are non-parametric in a way that they’ve infinite variety of parameters. Since they’re handled in a Bayesian strategy we’re capable of assemble massive fashions with infinite parameters which we combine out to keep away from overfitting. It may be proven that DPs will be represented in numerous methods all of that are mathematically equal. Few widespread methods to symbolize a Dirichlet course of is with the Blackwell-MacQueen urn scheme, the Stick-breaking building and the Chinese language Restaurant Course of.
Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions will be constructed with a purpose to carry out clustering in units of knowledge. With DPMMs we assemble a single combination mannequin wherein the variety of combination elements is infinite. Because of this DPMM doesn’t require us to outline from the start the variety of clusters (which on this case it’s infinite) and it permits us to adapt the variety of energetic clusters as we feed extra information to our mannequin over time.
As we are going to see in an upcoming article, representing DPMM as a Chinese language Restaurant Course of creates a clustering impact which we use to carry out Cluster Evaluation on the information. So as to estimate the cluster assignments of our mannequin we will use Gibbs sampling and consequently we should choose the suitable conjugate priors to make the sampling potential.
5. Purposes of DPMMs
The Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions have turn out to be well-liked each in Machine Studying and in Statistics. Consequently they’ve been utilized in a big quantity or purposes. Wooden et al. have used DPMMs to carry out spike sorting and determine the variety of totally different neurons that had been monitored by a single electrode. Sudderth et al. have used this mannequin to carry out Visible Scene Evaluation and determine the variety of objects, components and options {that a} specific picture comprises. Liang et al. and Finkel et al. used Hierarchical Dirichlet processes within the discipline of Pure Language Processing with a purpose to detect what number of grammar symbols exist in a selected set of sentenses. Lastly Blei et al. and Teh et al. have used comparable hierarchical fashions with a purpose to cluster paperwork primarily based on their semantic classes.
6. Motivation
The DPMMs turn out to be increasigly well-liked and an energetic space of analysis. They’ve been utilized to a lot of totally different issues and clear up most of the aformentioned limitations of Cluster Evaluation inside the probabilistic framework. DPMMs enable us to carry out unsupervised studying through the use of non-parametric and fully-bayesian strategy and construct sophisticated fashions with Hierarchical construction.
Due to this fact on this sequence of articles I’ll deal with presenting the mathematical foundations of the mannequin, focus on the varied representations of Direclet Processes, introduce 2 totally different fashions the Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin and the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin that can be utilized for clustering steady information and paperwork and at last I’ll current my Java implementation and the outcomes of demos.
7. Upcoming Posts / Construction
This sequence of articles will comply with the identical construction as my analysis report and it is going to be organized within the following segments:
- Overview of Cluster Evaluation and Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions: Overview of varied Cluster Evaluation strategies and their purposes, description of the issue of estimating the variety of clusters and overview of DPMMs and their purposes.
- Finite Combination Mannequin primarily based on Dirichlet Distribution: Discusses the fundamentals of Beta and Dirichlet distributions, introduces the Dirichlet Prior with Multinomial Chance mannequin and the Finite Combination Mannequin with Dirichlet distribution.
- The Dirichlet Course of the Chinese language Restaurant Course of and different representations: Defines the Dirichlet Course of, presents the varied representations of DP and focuses on Chinese language Restaurant Course of.
- The Dirichlet Course of Combination Mannequin: Presents the Dirichlet Course of Combination Mannequin, supplies an alternate mannequin which makes use of the Chinese language Restaurant Course of and describes the Collapsed-Gibbs sampler which is used to estimate the cluster assignments.
- Clustering paperwork and gaussian information with Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions: Discusses learn how to carry out clustering through the use of DPMMs and presents the Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin and the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin.
- Clustering with Dirichlet Course of Combination Mannequin in Java: Offers an outline of my Java implementation of the Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin and the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin together with a demo.
Keep tuned for the upcoming articles! I hope you loved this publish; should you did please take a second to share the article on Fb and Twitter. 🙂