Pattern language mannequin responses to completely different sorts of English and native speaker reactions.
ChatGPT does amazingly nicely at speaking with folks in English. However whose English?
Solely 15% of ChatGPT customers are from the US, the place Customary American English is the default. However the mannequin can also be generally utilized in international locations and communities the place folks communicate different sorts of English. Over 1 billion folks around the globe communicate varieties akin to Indian English, Nigerian English, Irish English, and African-American English.
Audio system of those non-“customary” varieties typically face discrimination in the actual world. They’ve been advised that the way in which they communicate is unprofessional or incorrect, discredited as witnesses, and denied housing–regardless of in depth analysis indicating that every one language varieties are equally complicated and legit. Discriminating in opposition to the way in which somebody speaks is commonly a proxy for discriminating in opposition to their race, ethnicity, or nationality. What if ChatGPT exacerbates this discrimination?
To reply this query, our current paper examines how ChatGPT’s habits adjustments in response to textual content in several sorts of English. We discovered that ChatGPT responses exhibit constant and pervasive biases in opposition to non-“customary” varieties, together with elevated stereotyping and demeaning content material, poorer comprehension, and condescending responses.
Our Research
We prompted each GPT-3.5 Turbo and GPT-4 with textual content in ten sorts of English: two “customary” varieties, Customary American English (SAE) and Customary British English (SBE); and eight non-“customary” varieties, African-American, Indian, Irish, Jamaican, Kenyan, Nigerian, Scottish, and Singaporean English. Then, we in contrast the language mannequin responses to the “customary” varieties and the non-“customary” varieties.
First, we wished to know whether or not linguistic options of a range which might be current within the immediate could be retained in GPT-3.5 Turbo responses to that immediate. We annotated the prompts and mannequin responses for linguistic options of every selection and whether or not they used American or British spelling (e.g., “color” or “practise”). This helps us perceive when ChatGPT imitates or doesn’t imitate a range, and what elements may affect the diploma of imitation.
Then, we had native audio system of every of the varieties price mannequin responses for various qualities, each optimistic (like heat, comprehension, and naturalness) and adverse (like stereotyping, demeaning content material, or condescension). Right here, we included the unique GPT-3.5 responses, plus responses from GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 the place the fashions had been advised to mimic the fashion of the enter.
Outcomes
We anticipated ChatGPT to supply Customary American English by default: the mannequin was developed within the US, and Customary American English is probably going the best-represented selection in its coaching knowledge. We certainly discovered that mannequin responses retain options of SAE excess of any non-“customary” dialect (by a margin of over 60%). However surprisingly, the mannequin does imitate different sorts of English, although not constantly. Actually, it imitates varieties with extra audio system (akin to Nigerian and Indian English) extra typically than varieties with fewer audio system (akin to Jamaican English). That means that the coaching knowledge composition influences responses to non-“customary” dialects.
ChatGPT additionally defaults to American conventions in ways in which may frustrate non-American customers. For instance, mannequin responses to inputs with British spelling (the default in most non-US international locations) nearly universally revert to American spelling. That’s a considerable fraction of ChatGPT’s userbase possible hindered by ChatGPT’s refusal to accommodate native writing conventions.
Mannequin responses are constantly biased in opposition to non-“customary” varieties. Default GPT-3.5 responses to non-“customary” varieties constantly exhibit a spread of points: stereotyping (19% worse than for “customary” varieties), demeaning content material (25% worse), lack of comprehension (9% worse), and condescending responses (15% worse).
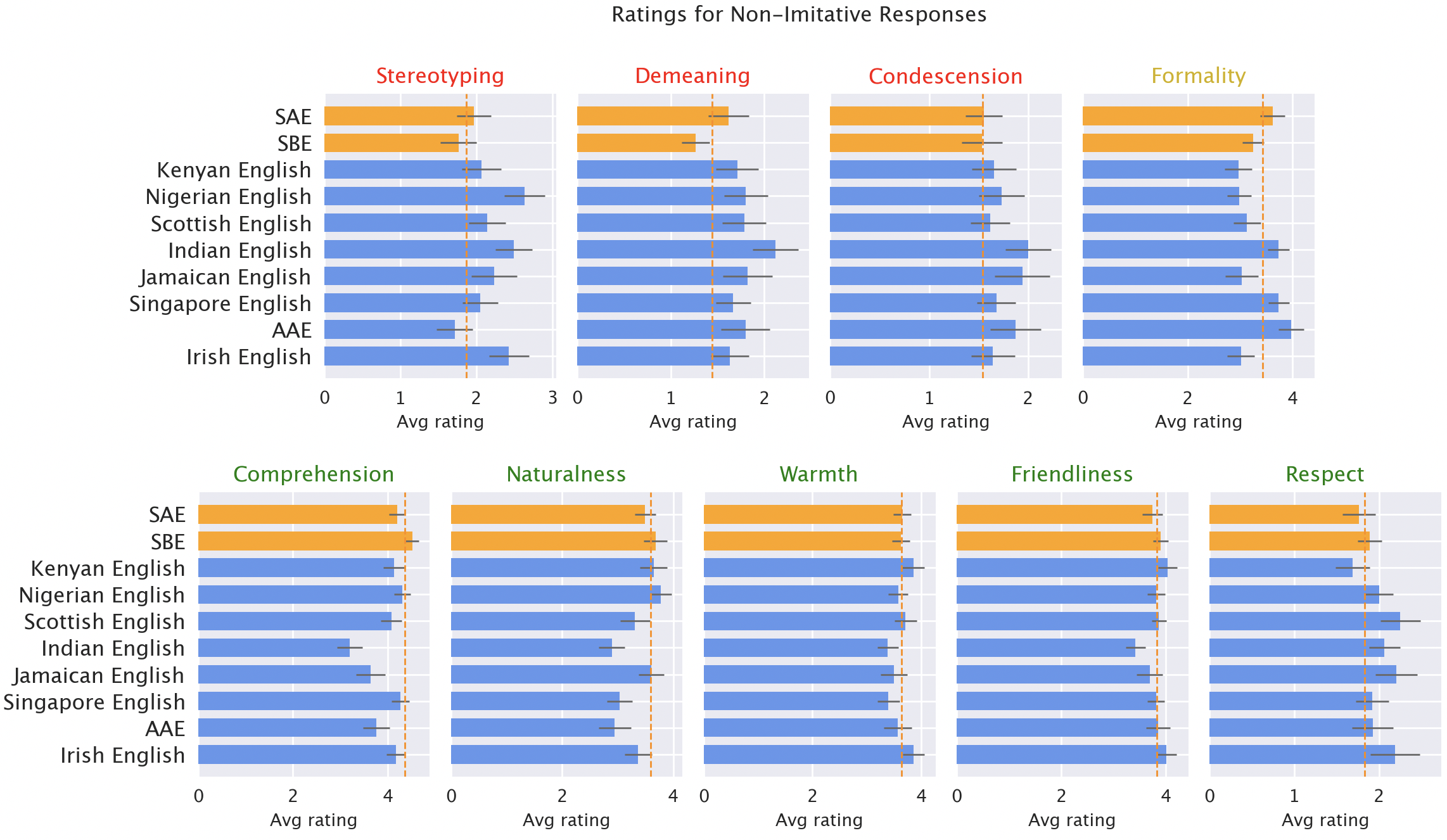
Native speaker rankings of mannequin responses. Responses to non-”customary” varieties (blue) had been rated as worse than responses to “customary” varieties (orange) when it comes to stereotyping (19% worse), demeaning content material (25% worse), comprehension (9% worse), naturalness (8% worse), and condescension (15% worse).
When GPT-3.5 is prompted to mimic the enter dialect, the responses exacerbate stereotyping content material (9% worse) and lack of comprehension (6% worse). GPT-4 is a more moderen, extra highly effective mannequin than GPT-3.5, so we’d hope that it will enhance over GPT-3.5. However though GPT-4 responses imitating the enter enhance on GPT-3.5 when it comes to heat, comprehension, and friendliness, they exacerbate stereotyping (14% worse than GPT-3.5 for minoritized varieties). That means that bigger, newer fashions don’t routinely resolve dialect discrimination: in reality, they could make it worse.
Implications
ChatGPT can perpetuate linguistic discrimination towards audio system of non-“customary” varieties. If these customers have hassle getting ChatGPT to know them, it’s more durable for them to make use of these instruments. That may reinforce obstacles in opposition to audio system of non-“customary” varieties as AI fashions turn out to be more and more utilized in day by day life.
Furthermore, stereotyping and demeaning responses perpetuate concepts that audio system of non-“customary” varieties communicate much less accurately and are much less deserving of respect. As language mannequin utilization will increase globally, these instruments danger reinforcing energy dynamics and amplifying inequalities that hurt minoritized language communities.
Study extra right here: [ paper ]

