On this information, we are going to stroll via making a 2-node or 4-node Hyper-V failover cluster the place the nodes are not domain-joined, utilizing mutual certificate-based authentication as a substitute of NTLM or shared native accounts. Right here we’re going to leverage X.509 certificates for node-to-node authentication. Should you do not use certificates, you are able to do this with NTLM, however we’re avoiding that as NTLM is supported, however the common advice is that you just deprecate it the place you may. We won’t use Kerberos as a result of our nodes will not be area joined.
It is lots simpler to do Home windows Server Clusters if every little thing is area joined, however that is not what we’re doing right here as a result of there are eventualities the place folks need every cluster node to be a standalone (in all probability why you might be studying this text).
Earlier than diving into configuration, guarantee the next conditions and baseline setup:
- Server OS and Roles: All cluster nodes should be working Home windows Server 2025 (similar version and patch degree). Set up the most recent updates and drivers on every node. Every node ought to have the Hyper-V function and Failover Clustering characteristic obtainable (we are going to set up these by way of PowerShell shortly).
- Workgroup configuration: Nodes should be in a workgroup. The nodes ought to be in the identical workgroup identify. All nodes ought to share a standard DNS suffix in order that they will resolve one another’s FQDNs. For instance, in case your chosen suffix is mylocal.web, guarantee every server’s FQDN is NodeName.mylocal.web.
- Identify Decision: Present a approach for nodes to resolve one another’s names (and the cluster identify). You probably have no inside DNS server, use the hosts file on every node to map hostnames to IPs. At minimal, add entries for every node’s identify (brief and FQDN) and the deliberate cluster identify (e.g. Cluster1 and Cluster1.mylocal.web) pointing to the cluster’s administration IP tackle.
- Community configuration: Guarantee a dependable, low-latency community hyperlinks all nodes. Ideally use a minimum of two networks or VLANs: one for administration/cluster communication and one devoted for Reside Migration site visitors. This improves efficiency and safety (reside migration site visitors will be remoted). If utilizing a single community, guarantee it’s a trusted, personal community since reside migration information isn’t encrypted by default. Assign static IPs (or DHCP reservations) on the administration community for every node and resolve on an unused static IP for the cluster itself. Confirm that needed firewall guidelines for clustering are enabled on every node (Home windows will add these when the Failover Clustering characteristic is put in, but when your community is classed Public, you could must allow them or set the community location to Personal).
- Time synchronization: Constant time is essential for certificates belief. Configure NTP on every server (e.g. pointing to a dependable web time supply or a neighborhood NTP server) in order that system clocks are in sync.
- Shared storage: Put together the shared storage that every one nodes will use for Hyper-V. This may be an iSCSI goal or an SMB 3.0 share accessible to all nodes. For iSCSI or SAN storage, join every node to the iSCSI goal (e.g. utilizing the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator) and current the identical LUN(s) to all nodes. Don’t convey the disks on-line or format them on particular person servers – depart them uncooked for the cluster to handle. For an SMB 3 file share, make sure the share is configured for steady availability. Observe: A file share witness for quorum is not supported in a workgroup cluster, so plan to make use of a disk witness or cloud witness as a substitute.
- Administrative entry: You will want Administrator entry to every server. Whereas we are going to keep away from utilizing similar native consumer accounts for cluster authentication, you need to nonetheless have a option to log into every node (e.g. the built-in native Administrator account on every machine). If utilizing Distant Desktop or PowerShell Remoting for setup, guarantee you may authenticate to every server (we are going to configure certificate-based WinRM for safe distant PowerShell). The cluster creation course of will be completed by working instructions regionally on every node to keep away from passing NTLM credentials.
The core of our setup is the usage of mutual certificate-based authentication between cluster nodes. Every node will want an X.509 certificates that the others belief. We’ll define the best way to use an inside Lively Listing Certificates Providers (AD CS) enterprise CA to challenge these certificates, and point out options for check environments. We’re utilizing AD CS regardless that the nodes aren’t area joined. Simply because the nodes aren’t members of the area does not imply you may’t use an Enterprise CA to challenge certificates, you simply have to make sure the nodes are configured to belief the CA’s certs manually.
Certificates Necessities and Template Configuration
For clustering (and associated options like Hyper-V reside migration) to authenticate utilizing certificates, the certificates should meet particular necessities:
- Key Utilization: The certificates ought to help digital signature and key encipherment (these are sometimes enabled by default for SSL certificates).
- Enhanced Key Utilization (EKU): It should embody each Consumer Authentication and Server Authentication EKUs. Having each permits the certificates to be offered by a node as a shopper (when initiating a connection to a different node) and as a server (when accepting a connection). For instance, within the certificates’s properties you need to see Consumer Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) and Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1) listed below “Enhanced Key Utilization”.
- Topic Identify and SAN: The certificates’s topic or Topic Various Identify ought to embody the node’s DNS identify. It is strongly recommended that the Topic Widespread Identify (CN) be set to the server’s totally certified DNS identify (e.g. Node1.mylocal.web). Additionally embody the brief hostname (e.g. Node1) within the Topic Various Identify (SAN) extension (DNS entries). You probably have already chosen a cluster identify (e.g. Cluster1), embody the cluster’s DNS identify within the SAN as effectively. This ensures that any node’s certificates can be utilized to authenticate connections addressed to the cluster’s identify or the node’s identify. (Together with the cluster identify in all node certificates is non-compulsory however can facilitate administration entry by way of the cluster identify over HTTPS, since whichever node responds will current a certificates that matches the cluster identify in SAN.)
- Belief: All cluster nodes should belief the issuer of the certificates. If utilizing an inside enterprise CA, this implies every node ought to have the CA’s root certificates in its Trusted Root Certification Authorities retailer. If you’re utilizing a standalone or third-party CA, equally guarantee the basis (and any intermediate CA) is imported into every node’s Trusted Root retailer.
Subsequent, in your enterprise CA, create a certificates template for the cluster node certificates (or use an applicable present template):
- Template foundation: A superb start line is the built-in “Laptop” or “Net Server” template. Duplicate the template so you may modify settings with out affecting defaults.
- Basic Settings: Give the brand new template a descriptive identify (e.g. “Workgroup Cluster Node”). Set the validity interval (e.g. 1 or 2 years – plan a manageable renewal schedule since these certs will want renewal sooner or later).
- Compatibility: Guarantee it’s set for a minimum of Home windows Server 2016 or increased for each Certification Authority and Certificates Recipient to help fashionable cryptography.
- Topic Identify: Since our servers should not domain-joined (and thus can’t auto-enroll with their AD laptop identify), configure the template to enable topic identify provide within the request. Within the template’s Topic Identify tab, select “Provide in request” (this enables us to specify the SAN and CN once we request the cert on every node). Alternatively, use the SAN area within the request – fashionable certificates requests will sometimes put the FQDN within the SAN.
- Extensions: Within the Extensions tab, edit Key Utilization to make sure it contains Digital Signature and Key Encipherment (these ought to already be chosen by default for Laptop templates). Then edit Prolonged Key Utilization and ensure Consumer Authentication and Server Authentication are current. If utilizing a duplicated Net Server template, add Consumer Authentication EKU; if utilizing Laptop template, each EKUs ought to already be there. Additionally allow personal key export in case your coverage requires (although typically personal keys shouldn’t be exported; right here every node may have its personal cert so export isn’t needed apart from backup functions).
- Safety: Enable the account that will likely be requesting the certificates to enroll. For the reason that nodes should not in AD, you may generate the CSR on every node after which submit it by way of an admin account. One strategy is to make use of a domain-joined administration PC or the CA server itself to submit the CSR, so guarantee area customers (or a particular consumer) have Enroll permission on the template.
- Publish the template: On the CA, publish the brand new template so it’s obtainable for issuing.
Acquiring Certificates from the Enterprise CA
Now for every cluster node, request a certificates from the CA utilizing the brand new template. To do that, on every node, create an INF file describing the certificates request. For instance, Node1.inf may specify the Topic as CN=Node1.mylocal.web and embody SANs for Node1.mylocal.web, Node1, Cluster1.mylocal.web, Cluster1. Additionally specify within the INF that you really want Consumer and Server Auth EKUs (or for the reason that template has them by default, it may not be wanted to checklist them explicitly). Then run:
certreq -new Node1.inf Node1.req
This generates a CSR file (Node1.req). Switch this request to a machine the place you may attain the CA (or use the CA net enrollment). Submit the request to your CA, specifying the customized template. For instance:
certreq -submit -attrib "CertificateTemplate:Workgroup Cluster Node" Node1.req Node1.cer
(Or use the Certification Authority MMC to approve the pending request.) This yields Node1.cer. Lastly, import the issued certificates on Node1:
certreq -accept Node1.cer
It will robotically place the certificates within the Native Machine Private retailer with the personal key.
- Utilizing Certificates MMC (if the CA net portal is offered): On every node, open Certificates (Native Laptop) MMC and below Private > Certificates, provoke New Certificates Request. Use the Lively Listing Enrollment Coverage if the node can attain the CA’s net enrollment (even when not domain-joined, you may usually authenticate with a website consumer account for enrollment). Choose the customized template and provide the DNS names. Full the enrollment to acquire the certificates within the Private retailer.
- On a domain-joined helper system: Alternatively, use a domain-joined machine to request on behalf of the node (utilizing the “Enroll on behalf” characteristic with an Enrollment Agent certificates, or just request after which export/import). That is extra complicated and normally not wanted until coverage restricts direct enrollment.
After acquiring every certificates, confirm on the node that it seems in Certificates (Native Laptop) > Private > Certificates. The Issued To ought to be the node’s FQDN, and on the Particulars tab you need to see the required EKUs and SAN entries. Additionally import the CA’s Root CA certificates into Trusted Root Certification Authorities on every node (the certreq -accept step might do that robotically if the chain is offered; if not, manually import the CA root). A fast examine utilizing the Certificates MMC or PowerShell can verify belief. For instance, to examine by way of PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem Cert:LocalMachineMy | The place-Object {$_.Topic -like "*Node1*"} | Choose-Object Topic, EnhancedKeyUsageList, NotAfter
Be certain the EnhancedKeyUsageList exhibits each Consumer and Server Authentication and that NotAfter (expiry) is an inexpensive date. Additionally guarantee no errors about untrusted issuer – the Certificates standing ought to present “This certificates is OK”.
Choice: Self-Signed Certificates for Testing
For a lab or proof-of-concept (the place an enterprise CA isn’t obtainable), you should use self-signed certificates. The secret’s to create a self-signed cert that features the right names and EKUs, after which belief that cert throughout all nodes. Use PowerShell New-SelfSignedCertificate with applicable parameters. For instance, on Node1:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName "Node1.mylocal.web", "Node1", "Cluster1.mylocal.web", "Cluster1" `
-CertStoreLocation Cert:LocalMachineMy `
-KeyUsage DigitalSignature, KeyEncipherment `
-TextExtension @("2.5.29.37={textual content}1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1;1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2")
This creates a certificates for Node1 with the desired DNS names and each ServerAuth/ClientAuth EKUs. Repeat on Node2 (adjusting names accordingly). Alternatively, you may generate a short-term root CA certificates after which challenge baby certificates to every node (PowerShell’s -TestRoot change simplifies this by producing a root and end-entity cert collectively).
Should you created particular person self-signed certs per node, export every node’s certificates (with out the personal key) and import it into the Trusted Folks or Trusted Root retailer of the different nodes. (Trusted Folks works for peer belief of particular certs; Trusted Root works should you created a root CA and issued from it). For instance, if Node1 and Node2 every have self-signed certs, import Node1’s cert as a Trusted Root on Node2 and vice versa. That is required as a result of self-signed certs should not robotically trusted.
Utilizing CA-issued certs is strongly advisable for manufacturing. Self-signed certs ought to solely be utilized in check environments, and if used, monitor and manually renew them earlier than expiration (since there’s no CA to do it). Quite a lot of issues have occurred in manufacturing techniques as a result of folks used self signed certs and forgot that they expire.
With certificates in place, we are able to configure Home windows Distant Administration (WinRM) to make use of them. WinRM is the service behind PowerShell Remoting and plenty of distant administration instruments. By default, WinRM makes use of HTTP (port 5985) and authenticates by way of Kerberos or NTLM. In a workgroup state of affairs, NTLM over HTTP could be used – we need to keep away from that. As an alternative, we are going to allow WinRM over HTTPS (port 5986) with our certificates, offering encryption and the power to make use of certificate-based authentication for administration classes.
Carry out these steps on every cluster node:
- Confirm certificates for WinRM: WinRM requires a certificates within the Native Laptop Private retailer that has a Server Authentication EKU and whose Topic or SAN matches the hostname. We’ve got already enrolled such a certificates for every node. Double-check that the certificates’s Issued To (CN or one of many SAN entries) precisely matches the hostname that shoppers will use (e.g. the FQDN). Should you plan to handle by way of brief identify, make sure the brief identify is in SAN; if by way of FQDN, that’s lined by CN or SAN. The certificates should not be expired or revoked, and it ought to be issued by a CA that the shoppers belief (not self-signed until the shopper trusts it).
- Allow the HTTPS listener: Open an elevated PowerShell on the node and run:
winrm quickconfig -transport:https
This command creates a WinRM listener on TCP 5986 sure to the certificates. If it says no certificates was discovered, you could must specify the certificates manually. You are able to do so with:
# Discover the certificates thumbprint (assuming just one with Server Auth)
$thumb = (Get-ChildItem Cert:LocalMachineMy | The place-Object {$_.EnhancedKeyUsageList -match "Server Authentication"} | Choose-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty Thumbprint)
New-Merchandise -Path WSMan:LocalHostListener -Transport HTTPS -Tackle * -CertificateThumbprint $thumb -Power
Confirm listeners with:
winrm enumerate winrm/config/listener
It is best to see an HTTPS listener with hostname, listening on 5986, and the certificates’s thumbprint. WinRM will robotically select a certificates that meets the factors (if a number of are current, it picks the one with CN matching machine identify, so ideally use a singular cert to keep away from ambiguity).
Disable unencrypted/HTTP entry (non-compulsory however advisable): Since we wish all distant administration encrypted and to remove NTLM, you may disable the HTTP listener. Run:
Take away-WSManInstance -ResourceURI winrm/config/Listener -SelectorSet @{Tackle="*", Transport="HTTP"}
This ensures WinRM is simply listening on HTTPS. Additionally, you could configure the WinRM service to reject unencrypted site visitors and disallow Primary authentication to stop any fallback to insecure strategies:
winrm set winrm/config/service '@{AllowUnencrypted="false"}'winrm set winrm/config/service/auth '@{Primary="false"}'
(By default, AllowUnencrypted is fake anyway when HTTPS is used, and Primary is fake until explicitly enabled.)
TrustedHosts (if wanted): In a workgroup, WinRM gained’t robotically belief hostnames for authentication. Nonetheless, when utilizing certificates authentication, the same old TrustedHosts requirement might not apply in the identical approach as for NTLM/Negotiate. Should you plan to authenticate with username/password over HTTPS (e.g. utilizing Primary or default CredSSP), you have to so as to add the opposite nodes (or administration station) to the TrustedHosts checklist on every node. This isn’t wanted for the cluster’s inside communication (which makes use of certificates by way of clustering, not WinRM), but it surely may be wanted to your distant PowerShell classes relying on methodology. To permit all (not advisable for safety), you can do:
Set-Merchandise WSMan:localhostClientTrustedHosts -Worth "*"
Or specify every host:
Set-Merchandise WSMan:localhostClientTrustedHosts -Worth "Node1,Node2,Cluster1"
This setting permits the native WinRM shopper to speak to these distant names with out Kerberos. If you’ll use certificate-based authentication for WinRM (the place the shopper presents a cert as a substitute of username/password), TrustedHosts isn’t required – certificates auth doesn’t depend on host belief in the identical approach.
(Non-compulsory) Configure certificates authentication for admin entry: One of many advantages of HTTPS listener is you should use certificates mapping to log in with no password. For superior customers, you may challenge a shopper certificates for your self (with Consumer Authentication EKU), then configure every server to map that cert to a consumer (for instance, map to the native Administrator account). This entails making a mapping entry in winrm/config/service/certmapping. As an example:
# Instance: map a shopper cert by its topic to a neighborhood accountwinrm create winrm/config/service/certmapping @{CertificateIssuer= "CN=YourCA"; Topic="CN=AdminUserCert"; Username="Administrator"; Password="
"; Enabled="true"}
Then out of your administration machine, you should use that certificates to authenticate. Whereas highly effective, this goes past the core cluster setup, so we gained’t element it additional. With out this, you may nonetheless connect with the nodes utilizing Enter-PSSession -ComputerName Node1 -UseSSL -Credential Node1Administrator (which can immediate for the password however ship it safely over the encrypted channel).
At this level, we’ve every node ready with a trusted certificates and WinRM listening securely. Check the connectivity: from one node, attempt to begin a PowerShell distant session to the opposite utilizing HTTPS. For instance, on Node1 run:
Check-WsMan Node2 -UseSSL
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName Node2 -UseSSL -Credential Node2Administrator
It is best to join with out credential errors or warnings (you could get a certificates belief immediate if the shopper machine doesn’t belief the server cert — be certain that the CA root is within the shopper’s belief retailer as effectively). As soon as you may handle nodes remotely over HTTPS, you’re able to create the cluster.
All cluster nodes want the Hyper-V function (for working VMs) and the Failover Clustering characteristic. We’ll use PowerShell to put in these concurrently on every server. On every node: Open an elevated PowerShell (regionally or by way of your new WinRM setup) and run:
Set up-WindowsFeature -Identify Failover-Clustering, Hyper-V -IncludeManagementTools -Restart
This installs the Hyper-V hypervisor, the clustering characteristic, and administration instruments (together with the Failover Cluster Supervisor and Hyper-V Supervisor GUI, and PowerShell modules). The server will restart if Hyper-V was not beforehand enabled (we embody -Restart for comfort). After reboot, run the command on the following node (if doing it remotely, do one after the other). Alternatively, use the Server Supervisor GUI or Set up-WindowsFeature with out -Restart and reboot manually. In spite of everything nodes are again up, confirm the options:
Get-WindowsFeature -Identify Hyper-V, Failover-Clustering
It ought to present each as Put in. Additionally verify the Failover Clustering PowerShell module is offered (Get-Module -ListAvailable FailoverClusters) and the Cluster service is put in (although not but configured).
Cluster service account: Home windows Server 2016+ robotically creates a neighborhood account known as CLIUSR utilized by the cluster service for inside communication. Guarantee this account was created (Laptop Administration > Customers). We gained’t work together with it immediately, however bear in mind it exists. Do not delete or disable CLIUSR – the cluster makes use of it alongside certificates for bootstrapping. (All cluster node communications will now use both Kerberos or certificates auth; NTLM isn’t wanted in WS2019+ clusters.)
Now that you have backflipped and shenaniganed with all of the certificates, you may really get round to constructing the cluster.
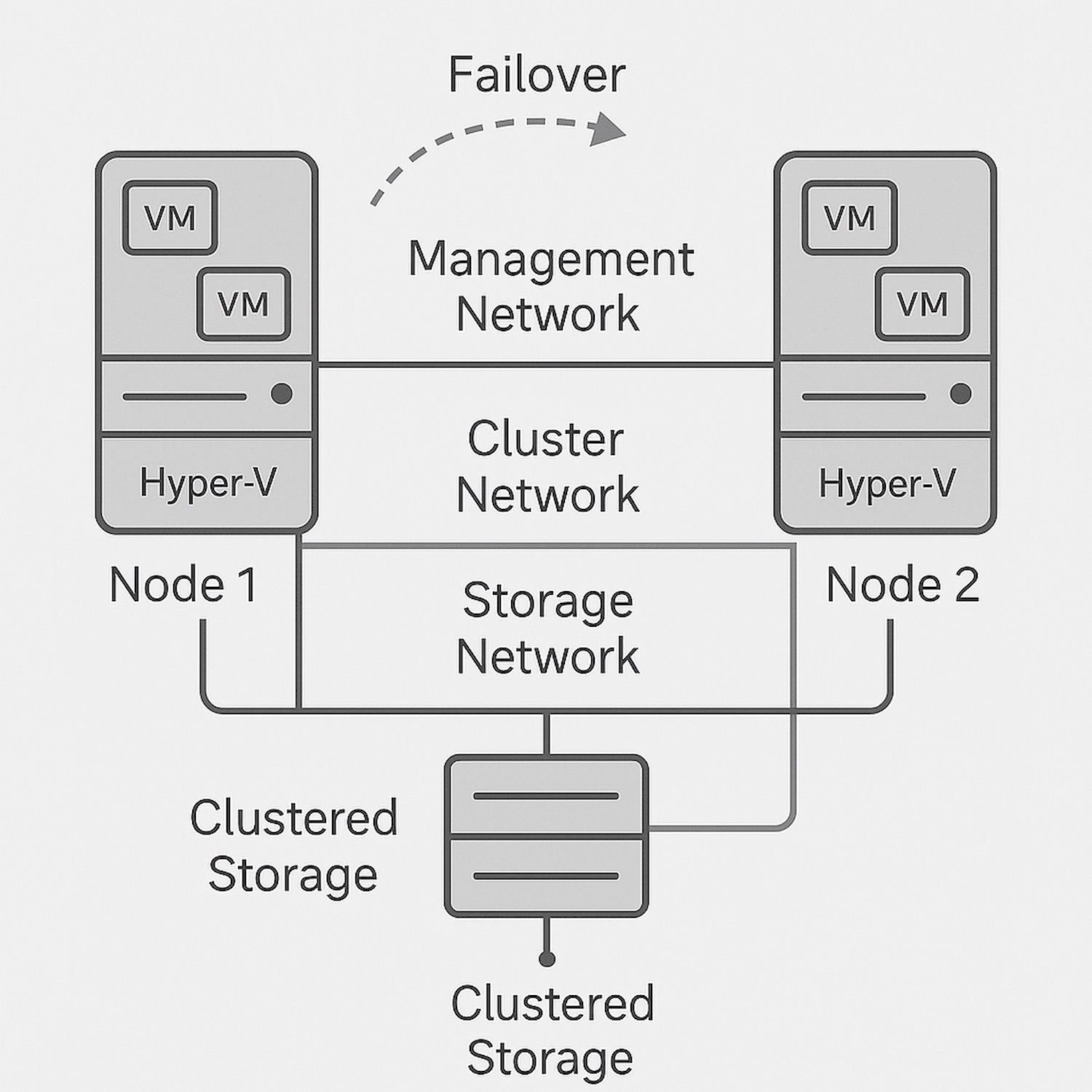
Right here we are going to create the cluster and add nodes to it utilizing PowerShell. The cluster will use a DNS identify for its administrative entry level (since there is no such thing as a Lively Listing for a conventional cluster laptop object). The fundamental steps are:
- Validate the configuration (non-compulsory however advisable).
- Create the cluster (initially with one node to keep away from cross-node authentication points).
- Be a part of extra node(s) to the cluster.
- Configure cluster networking, quorum, and storage (CSV).
Validate the Configuration (Cluster Validation)
It’s good follow to run the cluster validation exams to catch any misconfiguration or {hardware} points earlier than creating the cluster. Microsoft helps a cluster provided that it passes validation or if any errors are acknowledged as non-critical.
Run the next from one of many nodes (this can attain out to all nodes):
Check-Cluster -Node Node1.mylocal.web, Node2.mylocal.web
Exchange along with your precise node names (embody all 2 or 4 nodes). The cmdlet will run a sequence of exams (community, storage, system settings). Be certain that all exams both cross or solely have warnings that you just perceive. For instance, warnings about “no storage is shared amongst all nodes” are anticipated should you haven’t but configured iSCSI or if utilizing SMB (you may skip storage exams with -Skip Storage if wanted). If vital exams fail, resolve these points (networking, disk visibility, and so on.) earlier than continuing.
Create the Cluster (with the First Node)
On one node (say Node1), use the New-Cluster cmdlet to create the cluster with that node as the primary member. By doing it with a single node initially, we keep away from distant authentication at cluster creation time (no want for Node1 to authenticate to Node2 but):
New-Cluster -Identify "Cluster1" -Node Node1 -StaticAddress "10.0.0.100" -AdministrativeAccessPoint DNS
Right here:
- -Identify is the meant cluster identify (this would be the identify shoppers use to hook up with the cluster, e.g. for administration or as a CSV namespace prefix). We use “Cluster1” for instance.
- -Node Node1 specifies which server to incorporate initially (Node1’s identify).
- -StaticAddress units the cluster’s IP tackle (select one in the identical subnet that’s not in use; this IP will likely be introduced on-line because the “Cluster Identify” useful resource). On this instance 10.0.0.100 is the cluster IP.
- -AdministrativeAccessPoint DNS signifies we’re making a DNS-only cluster (no AD laptop object). That is the default in workgroup clusters, however we specify it explicitly for readability.
The command will proceed to create the cluster service, register the cluster identify in DNS (if DNS is configured and dynamic updates allowed), and convey the core cluster sources on-line. It would additionally create a cluster-specific certificates (self-signed) for inside use if wanted, however since we’ve our CA-issued certs in place, the cluster might use these for node authentication.
Observe: If New-Cluster fails to register the cluster identify in DNS (widespread in workgroup setups), you may must create a handbook DNS A document for “Cluster1” pointing to 10.0.0.100 in no matter DNS server the nodes use. Alternatively, add “Cluster1” to every node’s hosts file (as we did in conditions). This ensures that the cluster identify is resolvable. The cluster will operate with out AD, but it surely nonetheless depends on DNS for identify decision of the cluster identify and node names.
At this level, the cluster exists with one node (Node1). You’ll be able to confirm by working cluster cmdlets on Node1, for instance: Get-Cluster (ought to checklist “Cluster1”) and Get-ClusterNode (ought to checklist Node1 as up). In Failover Cluster Supervisor, you can additionally connect with “Cluster1” (or to Node1) and see the cluster.
Add Extra Nodes to the Cluster
Now we are going to add the remaining node(s) to the cluster:
On every extra node, run the next (substitute “Node2” with the identify of that node and regulate cluster identify accordingly):
Add-ClusterNode -Cluster Cluster1 -Identify Node2
Run this on Node2 itself (regionally). This instructs Node2 to affix the cluster named Cluster1. As a result of Node2 can authenticate the cluster (Node1) by way of the cluster’s certificates and vice versa, the be part of ought to succeed with out prompting for credentials. Beneath the hood, the cluster service on Node2 will use the certificates (and CLIUSR account) to ascertain belief with Node1’s cluster service.
Repeat the Add-ClusterNode command on every extra node (Node3, Node4, and so on. one after the other). After every be part of, confirm by working Get-ClusterNode on any cluster member – the brand new node ought to present up and standing “Up”.
If for some motive you like a single command from Node1 so as to add others, you can use:
# Run on Node1:Add-ClusterNode -Identify Node2, Node3 -Cluster Cluster1
This is able to try so as to add Node2 and Node3 from Node1. It might immediate for credentials or require TrustedHosts if no widespread auth is current. Utilizing the native Add-ClusterNode on every node avoids these points by performing the motion regionally. Both approach, on the finish all nodes ought to be members of Cluster1.
Quorum configuration is vital, particularly with an excellent variety of nodes. The cluster will already default to Node Majority (no witness) or might attempt to assign a witness if it finds eligible storage.
Use a witness to keep away from a split-brain state of affairs. You probably have a small shared disk (LUN) seen to each nodes, that may be a Disk Witness. Alternatively, use a Cloud Witness (Azure). To configure a disk witness, first be certain that the disk is seen as Out there Storage within the cluster, then run:
Get-ClusterAvailableDisk | Add-ClusterDiskSet-ClusterQuorum -Cluster Cluster1 -NodeAndDiskMajority 0 /disk:
(Exchange
Set-ClusterQuorum -Cluster Cluster1 -CloudWitness -AccountName "" -AccessKey " "
Don’t use a File Share witness – as famous earlier, file share witnesses should not supported in workgroup clusters as a result of the cluster can’t authenticate to a distant share with out AD.
A 4-node cluster can maintain two node failures if correctly configured. It’s advisable to additionally configure a witness for even-number clusters to keep away from a tie (2–2) throughout a dual-node failure state of affairs. A disk or cloud witness is advisable (similar course of as above). With 4 nodes, you’d sometimes use Node Majority + Witness. The cluster quorum wizard can robotically select the very best quorum config (sometimes it’ll choose Node Majority + Witness should you run the wizard and have a witness obtainable).
You’ll be able to confirm the quorum configuration with Get-ClusterQuorum. Be certain it lists the witness you configured (if any) and that the cluster core sources present the witness on-line.
Add Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) or Configure VM Storage
Subsequent, put together storage for Hyper-V VMs. If utilizing a shared disk (Block storage like iSCSI/SAN), after including the disks to the cluster (they need to seem in Storage > Disks in Failover Cluster Supervisor), you may allow Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV). CSV permits all nodes to concurrently entry the NTFS/ReFS quantity, simplifying VM placement and reside migration. So as to add obtainable cluster disks as CSV volumes:
Get-ClusterDisk | The place-Object IsClustered -eq $true | Add-ClusterSharedVolume
It will take every clustered disk and mount it as a CSV below C:ClusterStorage on all nodes. Alternatively, right-click the disk in Failover Cluster Supervisor and select Add to Cluster Shared Volumes. As soon as completed, format the amount (if not already formatted) with NTFS or ReFS by way of any node (will probably be accessible as C:ClusterStorageVolume1 and so on. on all nodes). Now this shared quantity can retailer all VM information, and any node can run any VM utilizing that storage.
If utilizing an SMB 3 share (NAS or file server), you gained’t add this to cluster storage; as a substitute, every Hyper-V host will connect with the SMB share immediately. Guarantee every node has entry credentials for the share. In a workgroup, that sometimes means the NAS can be in a workgroup and also you’ve created a neighborhood consumer on the NAS that every node makes use of (by way of saved credentials) – that is outdoors the cluster’s management. Every node ought to have the ability to New-SmbMapping or just entry the UNC path. Check entry from every node (e.g. Dir NASHyperVShare). In Hyper-V settings, you may set the Default Digital Arduous Disk Path to the UNC or simply specify the UNC when creating VMs. Observe: Hyper-V helps storing VMs on SMB 3.0 shares with Kerberos or certificate-based authentication, however in a workgroup you’ll seemingly depend on a username/password for the share (which is a type of native account utilization on the NAS). This doesn’t have an effect on cluster node-to-node auth, but it surely’s a consideration for securing the NAS.
At this stage, run some fast checks to make sure the cluster is wholesome:
- Get-Cluster – ought to present the cluster identify, IP, and core sources on-line.
- Get-ClusterNode – all nodes ought to be Up.
- Get-ClusterResource – ought to checklist sources (Cluster Identify, IP Tackle, any witness, any disks) and their state (On-line). The Cluster Identify useful resource will likely be of sort “Distributed Community Identify” since it is a DNS-only cluster.
- Use Failover Cluster Supervisor (you may launch it on one of many nodes or from RSAT on a shopper) to hook up with “Cluster1”. Guarantee you may see all nodes and storage. When prompted to attach, use
or – with our certificates setup, it might be finest to attach by cluster identify (be certain that DNS/hosts is resolving it to the cluster IP). If a certificates belief warning seems, it may be as a result of the administration station doesn’t belief the cluster node’s cert otherwise you related with a reputation not within the SAN. As a workaround, join on to a node in cluster supervisor (e.g. Node1), which then enumerates the cluster.
Now you may have a functioning cluster prepared for Hyper-V workloads, with safe authentication between nodes. Subsequent, we configure Hyper-V particular settings like Reside Migration.
One main profit launched in Home windows Server 2025 is help for Reside Migration in workgroup clusters (beforehand, reside migration required Kerberos and thus a website). In WS2025, cluster nodes use certificates to mutually authenticate for reside migration site visitors. This permits VMs to maneuver between hosts with no downtime even within the absence of AD. We’ll allow and tune reside migration for our cluster.
By default, the Hyper-V function might need reside migration disabled (for non-clustered hosts). In a cluster, it might be auto-enabled when the Failover Clustering and Hyper-V roles are each current, however to make sure it it, run:
Allow-VMMigration
This allows the host to ship/obtain reside migrations. In PowerShell, no output means success. (In Hyper-V Supervisor UI, this corresponds to ticking “Allow incoming and outgoing reside migrations” within the Reside Migrations settings.)
In a workgroup, the one alternative in UI could be CredSSP (since Kerberos requires area). CredSSP means you could provoke the migration from a session the place you might be logged onto the supply host so your credentials will be delegated. We can’t use Kerberos right here, however the cluster’s inside PKU2U certificates mechanism will deal with node-to-node auth for us when orchestrated by way of Failover Cluster Supervisor. No express setting is required for cluster-internal certificates utilization & Home windows will use it robotically for the precise reside migration operation. Should you have been to make use of PowerShell, the default MigrationAuthenticationType is CredSSP for workgroup. You’ll be able to verify (or set explicitly, although not strictly required):
Set-VMHost -VirtualMachineMigrationAuthenticationType CredSSP
(This may be completed on every node; it simply ensures the Hyper-V service is aware of to make use of CredSSP which aligns with our must provoke migrations from an authenticated context.)
In case your cluster nodes have been domain-joined, Home windows Server 2025 permits Credential Guard which blocks CredSSP by default. In our case (workgroup), Credential Guard isn’t enabled by default, so CredSSP will operate. Simply bear in mind should you ever be part of these servers to a website (or they have been as soon as joined to a website earlier than being demoted to a workgroup), you’d must configure Kerberos constrained delegation or disable Credential Guard to make use of reside migration.
For safety and efficiency, don’t use the administration community for VM migration you probably have different NICs. We’ll designate the devoted community (e.g. “LMNet” or a particular subnet) for migrations. You’ll be able to configure this by way of PowerShell or Failover Cluster Supervisor. Utilizing PowerShell, run the next on every node:
# Instance: enable LM solely on 10.0.1.0/24 community (the place 10.0.1.5 is that this node's IP on that community)
Set-VMMigrationNetwork 10.0.1.5
Set-VMHost -UseAnyNetworkForMigration $false
The Set-VMMigrationNetwork cmdlet provides the community related to the given IP to the allowed checklist for migrations. The second cmdlet ensures solely these designated networks are used. Alternatively, you probably have the community identify or interface identify, you may use Hyper-V Supervisor UI: below every host’s Hyper-V Settings > Reside Migrations > Superior Options, choose Use these IP addresses for Reside Migration and add the IP of the LM community interface. In a cluster, these settings are sometimes per-host. It’s a good suggestion to configure it identically on all nodes.
Confirm the community choice by working: Get-VMHost | Choose -ExpandProperty MigrationNetworks. It ought to checklist the subnet or community you allowed, and UseAnyNetworkForMigration ought to be False.
Home windows can both ship VM reminiscence over TCP, compress it, or use SMB Direct (if RDMA is offered) for reside migration. By default in newer Home windows variations, compression is used because it presents a stability of pace with out particular {hardware}. You probably have a really quick devoted community (10 Gbps+ or RDMA), you may select SMB to leverage SMB Multichannel/RDMA for highest throughput. To set this:
# Choices: TCPIP, Compression, SMB
Set-VMHost -VirtualMachineMigrationPerformanceOption Compression
(Do that on every node; “Compression” is normally default on 2022/2025 Hyper-V.) If you choose SMB, guarantee your cluster community is configured to permit SMB site visitors and contemplate enabling SMB encryption if safety is a priority (SMB encryption will encrypt the reside migration information stream). Observe that should you allow SMB encryption or cluster-level encryption, it might disable RDMA on that site visitors, so solely allow it if wanted, or depend on the community isolation as major safety.
Relying in your {hardware}, you could enable a number of VMs emigrate directly. The default is normally 2 simultaneous reside migrations. You’ll be able to improve this you probably have capability:
Set-VMHost -MaximumVirtualMachineMigrations 4 -MaximumStorageMigrations 2
Alter numbers as applicable (and contemplate that cluster-level property (Get-Cluster).MaximumParallelMigrations may override host setting in a cluster). This setting will also be present in Hyper-V Settings UI below Reside Migrations.
With these configured, reside migration is enabled.
Check a reside migration:
Create a check VM (or you probably have VMs, choose one) and try to maneuver it from one node to a different utilizing Failover Cluster Supervisor or PowerShell:
- In Failover Cluster Supervisor, below Roles, right-click a digital machine, select Reside Migrate > Choose Node… and choose one other node. The VM ought to migrate with zero downtime. If it fails, examine for error messages concerning authentication. Make sure you initiated the transfer from a node the place you’re an admin (or by way of cluster supervisor related to the cluster with applicable credentials). The cluster will deal with the mutual auth utilizing the certificates (that is clear – behind the scenes, the nodes use the self-created PKU2U cert or our put in certs to ascertain a safe connection for VM reminiscence switch).
- Alternatively, use PowerShell:
Transfer-ClusterVirtualMachineRole -Identify "" -Node
This cmdlet triggers a cluster-coordinated reside migration (the cluster’s Transfer operation will use the suitable auth). If the migration succeeds, congratulations – you may have a completely purposeful Hyper-V cluster with out AD!
Safety Finest Practices Recap and Extra Hardening
Extra finest practices for securing a workgroup Hyper-V cluster embody:
- Certificates Safety: The personal keys of your node certificates are highly effective – shield them. They’re saved within the machine retailer (and sure marked non-exportable). Solely admins can entry them; guarantee no unauthorized customers are within the native Directors group. Plan a course of for certificates renewal earlier than expiration. If utilizing an enterprise CA, you may challenge certificates with a template that enables auto-renewal by way of scripts or a minimum of monitor their expiry to re-issue and set up new certs on every node in time. The Failover Cluster service auto-generates its personal certificates (for CLIUSR/PKU2U) and auto-renews them, however since we offered our personal, we should handle these. Stagger renewals to keep away from all nodes swapping directly (the cluster ought to nonetheless belief previous vs new if the CA is similar). It might be clever to overlap: set up new certs on all nodes and solely then take away the previous, in order that at no level a node is presenting a cert the others do not settle for (should you change CA or template).
- Trusted Root and Revocation: All nodes belief the CA – preserve the safety of that CA. Don’t embody pointless belief (e.g., keep away from having nodes belief public CAs that they don’t want). If doable, use an inside CA that’s solely used for these infrastructure certs. Preserve CRLs (Certificates Revocation Lists) accessible in case your cluster nodes must examine revocation for one another’s certs (although cluster auth may not strictly require on-line revocation checking if the certificates are immediately trusted). It’s another excuse to have a fairly long-lived inside CA or offline root.
- Disable NTLM: Since clustering now not wants NTLM as of Home windows 2019+, you may contemplate disabling NTLM fallback on these servers solely for added safety (by way of Group Coverage “Community Safety: Prohibit NTLM: Deny on this server” and so on.). Nonetheless, be cautious: some processes (together with cluster formation in older variations, or different companies) may break. In our configuration, cluster communications ought to use Kerberos or cert. If these servers don’t have any want for NTLM (no legacy apps), disabling it eliminates a complete class of assaults. Monitor occasion logs (Safety log occasions for NTLM utilization) should you try this. The dialog within the Microsoft tech group signifies by WS2022, cluster ought to operate with NTLM disabled, although a consumer noticed points when CLIUSR password rotated if NTLM was blocked. WS2025 ought to additional scale back any NTLM dependency.
- PKU2U coverage: The cluster makes use of the PKU2U safety supplier for peer authentication with certificates. There’s a native safety coverage “Community safety: Enable PKU2U authentication requests to this laptop to make use of on-line identities” – this should be enabled (which it’s by default) for clustering to operate correctly. Some safety guides suggest disabling PKU2U; don’t disable it on cluster nodes (or in case your group’s baseline GPO disables it, create an exception for these servers). Disabling PKU2U will break the certificate-based node authentication and trigger cluster communication failures.
- Firewall: We opened WinRM over 5986. Guarantee Home windows Firewall has the Home windows Distant Administration (HTTPS-In) rule enabled. The Failover Clustering characteristic ought to have added guidelines for cluster heartbeats (UDP 3343, and so on.) and SMB (445) if wanted. Double-check that on every node the Failover Cluster group of firewall guidelines is enabled for the related profiles (in case your community is Public, you may must allow the foundations for Public profile manually, or set community as Personal). Additionally, for reside migration, if utilizing SMB transport, allow SMB-in guidelines. Should you enabled SMB encryption, it makes use of the identical port 445 however encrypts payloads.
- Safe Reside Migration Community: Ideally, the community carrying reside migration is remoted (not routed outdoors of the cluster atmosphere). If you’d like belt-and-suspenders safety, you can implement IPsec encryption on reside migration site visitors. For instance, require IPsec (with certificates) between the cluster nodes on the LM subnet. Nonetheless, this may be complicated and may battle with SMB Direct/RDMA. One other less complicated strategy: since we are able to depend on our certificates mutual auth to stop unauthorized node communication, concentrate on isolating that site visitors so even when somebody tapped it, you may optionally activate SMB encryption for LM (when utilizing SMB transport) which can encrypt the VM reminiscence stream. At minimal, deal with the LM community as delicate, because it carries VM reminiscence contents in clear textual content if not in any other case encrypted.
- Safe WinRM/administration entry: We configured WinRM for HTTPS. Be certain to restrict who can log in by way of WinRM. By default, members of the Directors group have entry. Don’t add pointless customers to Directors. You can too use Native Group Coverage to limit WinRM service to solely enable sure customers or certificates mappings. Since it is a workgroup, there’s no central AD group; you may create a neighborhood group for “Distant Administration Customers” and configure WSMan to permit members of that group (and solely put particular admin accounts in it). Additionally contemplate enabling PowerShell Simply Sufficient Administration (JEA) if you wish to delegate particular duties with out full admin rights, although that’s superior.
- Hyper-V host safety: Apply customary Hyper-V finest practices: allow Safe Boot for Gen2 VMs, hold the host OS minimal (think about using Home windows Server Core for fewer assault floor, if possible), and guarantee solely trusted directors can create or handle VMs. Since this cluster isn’t in a website, you gained’t have AD group-based entry management; think about using Authentication Insurance policies like LAPS for distinctive native admin passwords per node.
- Monitor cluster occasions: Monitor the System occasion log for any cluster-related errors (clustering will log occasions if authentication fails or if there are connectivity points). Additionally monitor the FailoverClustering occasion log channel. Any errors about “unable to authenticate” or “No logon servers” and so on., would point out certificates or connectivity issues.
- Check failover and failback: After configuration, check that VMs can failover correctly. Shut down one node and guarantee VMs transfer to different node robotically. When the node comes again, you may reside migrate them again. It will give confidence that the cluster’s certificate-based auth holds up below actual failover situations.
- Take into account Administration Instruments: Instruments like Home windows Admin Heart (WAC) can handle Hyper-V clusters. WAC will be configured to make use of the certificates for connecting to the nodes (it’ll immediate to belief the certificates if self-signed). Utilizing WAC or Failover Cluster Supervisor with our setup may require launching the console from a machine that trusts the cluster’s cert and utilizing the cluster DNS identify. All the time guarantee administration site visitors can be encrypted (WAC makes use of HTTPS and our WinRM is HTTPS so it’s).