- June 30, 2014
- Vasilis Vryniotis
- . No feedback
This text is the fifth a part of the tutorial on Clustering with DPMM. Within the earlier posts we lined intimately the theoretical background of the tactic and we described its mathematical representationsmu and methods to assemble it. On this submit we are going to attempt to hyperlink the speculation with the apply by introducing two fashions DPMM: the Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin which can be utilized to cluster Gaussian information and the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin which is used to cluster paperwork.
Replace: The Datumbox Machine Studying Framework is now open-source and free to obtain. Try the bundle com.datumbox.framework.machinelearning.clustering to see the implementation of Dirichlet Course of Combination Fashions in Java.
1. The Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin
The primary Dirichlet Course of combination mannequin that we are going to study is the Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin which can be utilized to carry out clustering on steady datasets. The combination mannequin is outlined as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Equation 1: Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin
As we are able to see above, the actual mannequin assumes that the Generative Distribution is the Multinomial Gaussian Distribution and makes use of the Chinese language Restaurant course of as prior for the cluster assignments. Furthermore for the Base distribution G0 it makes use of the Regular-Inverse-Wishart prior which is conjugate prior of Multivariate Regular distribution with unknown imply and covariance matrix. Beneath we current the Graphical Mannequin of the combination mannequin:
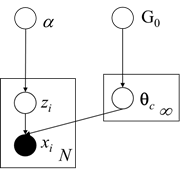
Determine 1: Graphical Mannequin of Dirichlet Multivariate Regular Combination Mannequin
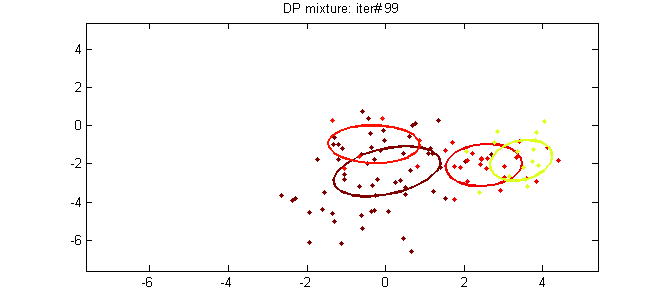
As we mentioned earlier, so as to have the ability to estimate the cluster assignments, we are going to use the Collapsed Gibbs sampling which requires choosing the acceptable conjugate priors. Furthermore we might want to replace the parameters posterior given the prior and the proof. Beneath we see the MAP estimates of the parameters for one of many clusters:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
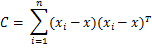
Equation 2: MAP estimates on Cluster Parameters
The place d is the dimensionality of our information and ![]() is the pattern imply. Furthermore we’ve a number of hyperparameters of the Regular-Inverse-Wishart such because the μ0 which is the preliminary imply, κ0 is the imply fraction which works as a smoothing parameter, ν0 is the levels of freedom which is about to the variety of dimensions and Ψ0 is the pairwise deviation product which is about to the dxd id matrix multiplied by a relentless. Any more all of the earlier hyperparameters of G0 might be denoted by λ to simplify the notation. Lastly by having all of the above, we are able to estimate the chances which can be required by the Collapsed Gibbs Sampler. The likelihood of remark i to belong to cluster okay given the cluster assignments, the dataset and all of the hyperparameters α and λ of DP and G0 is given under:
is the pattern imply. Furthermore we’ve a number of hyperparameters of the Regular-Inverse-Wishart such because the μ0 which is the preliminary imply, κ0 is the imply fraction which works as a smoothing parameter, ν0 is the levels of freedom which is about to the variety of dimensions and Ψ0 is the pairwise deviation product which is about to the dxd id matrix multiplied by a relentless. Any more all of the earlier hyperparameters of G0 might be denoted by λ to simplify the notation. Lastly by having all of the above, we are able to estimate the chances which can be required by the Collapsed Gibbs Sampler. The likelihood of remark i to belong to cluster okay given the cluster assignments, the dataset and all of the hyperparameters α and λ of DP and G0 is given under:
![]()
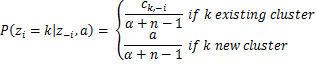
![]()
Equation 3: Chances utilized by Gibbs Sampler for MNMM
The place zi is the cluster task of remark xi, x1:n is the whole dataset, z-i is the set of cluster assignments with out the one of many ith remark, x-i is the whole dataset excluding the ith remark, cokay,-i is the overall variety of observations assigned to cluster okay excluding the ith remark whereas ![]() and
and ![]() are the imply and covariance matrix of cluster okay exluding the ith remark.
are the imply and covariance matrix of cluster okay exluding the ith remark.
2. The Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin
The Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin is used to carry out cluster evaluation of paperwork. The actual mannequin has a barely extra difficult hierarchy because it fashions the matters/classes of the paperwork, the phrase possibilities inside every matter, the cluster assignments and the generative distribution of the paperwork. Its goal is to carry out unsupervised studying and cluster an inventory of paperwork by assigning them to teams. The combination mannequin is outlined as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Equation 4: Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin
The place φ fashions the subject possibilities, zi is a subject selector, θokay are the phrase possibilities in every cluster and xi,j represents the doc phrases. We must always observe that this method makes use of the bag-of-words framework which represents the paperwork as an unordered assortment of phrases, disregarding grammar and phrase order. This simplified illustration is usually utilized in pure language processing and knowledge retrieval. Beneath we current the Graphical Mannequin of the combination mannequin:
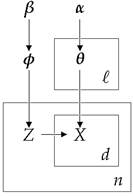
Determine 2: Graphical Mannequin of the Dirichlet-Multinomial Combination Mannequin
The actual mannequin makes use of Multinomial Discrete distribution for the generative distribution and Dirichlet distributions for the priors. The ℓ is the scale of our lively clusters, the n the overall variety of paperwork, the β controls the a priori anticipated variety of clusters whereas the α controls the variety of phrases assigned to every cluster. To estimate the chances which can be required by the Collapsed Gibbs Sampler we use the following equation:
![]()
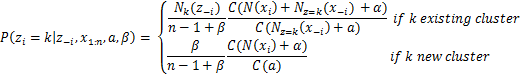
Equation 5: Chances utilized by Gibbs Sampler for DMMM
The place Γ is the gamma perform, zi is the cluster task of doc xi, x1:n is the whole dataset, z-i is the set of cluster assignments with out the one of many ith doc, x-i is the whole dataset excluding the ith doc, Nokay(z-i) is the variety of observations assigned to cluster okay excluding ith doc, Nz=okay(x-i) is a vector with the sums of counts for every phrase for all of the paperwork assigned to cluster okay excluding ith doc and N(xi) is the sparse vector with the counts of every phrase in doc xi. Lastly as we are able to see above, through the use of the Collapsed Gibbs Sampler with the Chinese language Restaurant Course of the θjk variable which shops the likelihood of phrase j in matter okay could be built-in out.