Think about going to the hospital for a bacterial ear an infection and listening to your physician say, “We’re out of choices.” It might sound dramatic, however antibiotic resistance is pushing that situation nearer to changing into actuality for an rising variety of individuals. In 2016, a girl from Nevada died from a bacterial an infection that was proof against all 26 antibiotics that had been out there in the USA at the moment.
The U.S. alone sees greater than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant diseases every year. Globally, antimicrobial resistance is linked to practically 5 million deaths yearly.
As resistant micro organism unfold, lifesaving remedies face new issues – widespread infections develop into more durable to deal with, and routine surgical procedures develop into riskier. Slowing these threats to fashionable medication requires not solely accountable antibiotic use and good hygiene, but in addition consciousness of how on a regular basis actions affect resistance.
For the reason that inception of antibiotics in 1910 with the introduction of Salvarsan, an artificial drug used to deal with syphilis, scientists have been sounding the alarm about resistance. As a microbiologist and biochemist who research antimicrobial resistance, I see 4 main tendencies that may form how we as a society will confront antibiotic resistance within the coming decade.
1. Quicker diagnostics are the brand new entrance line
For many years, treating bacterial infections has concerned a whole lot of educated guesswork. When a really sick affected person arrives on the hospital and clinicians don’t but know the precise micro organism inflicting the sickness, they typically begin with a broad-spectrum antibiotic. These medication kill many several types of micro organism directly, which could be lifesaving — however additionally they expose a variety of different micro organism within the physique to antibiotics. Whereas some micro organism are killed, those that stay proceed to multiply and unfold resistance genes between totally different bacterial species. That pointless publicity offers innocent or unrelated micro organism an opportunity to adapt and develop resistance.
In distinction, narrow-spectrum antibiotics goal solely a small group of micro organism. Clinicians usually favor these kinds of antibiotics as a result of they deal with the an infection with out disturbing micro organism that aren’t concerned within the an infection. Nevertheless, it might take a number of days to determine the precise micro organism inflicting the an infection. Throughout that ready interval, clinicians typically really feel they haven’t any alternative however to begin broad-spectrum remedy – particularly if the affected person is critically in poor health.
However new expertise might fast-track identification of bacterial pathogens, permitting medical assessments to be carried out proper the place the affected person is as a substitute of sending samples off-site and ready a very long time for solutions. As well as, advances in genomic sequencing, microfluidics and synthetic intelligence instruments are making it attainable to determine bacterial species and efficient antibiotics to combat them in hours moderately than days. Predictive instruments may even anticipate resistance evolution.
For clinicians, higher assessments might assist them make quicker diagnoses and more practical remedy plans that received’t exacerbate resistance. For researchers, these instruments level to an pressing must combine diagnostics with real-time surveillance networks able to monitoring resistance patterns as they emerge.
Diagnostics alone won’t clear up resistance, however they supply the precision, pace and early warning wanted to remain forward.
2. Increasing past conventional antibiotics
Antibiotics reworked medication within the twentieth century, however counting on them alone received’t carry humanity by means of the twenty first. The pipeline of recent antibiotics stays distressingly skinny, and most medication at the moment in improvement are structurally much like present antibiotics, doubtlessly limiting their effectiveness.
The antibiotic discovery void
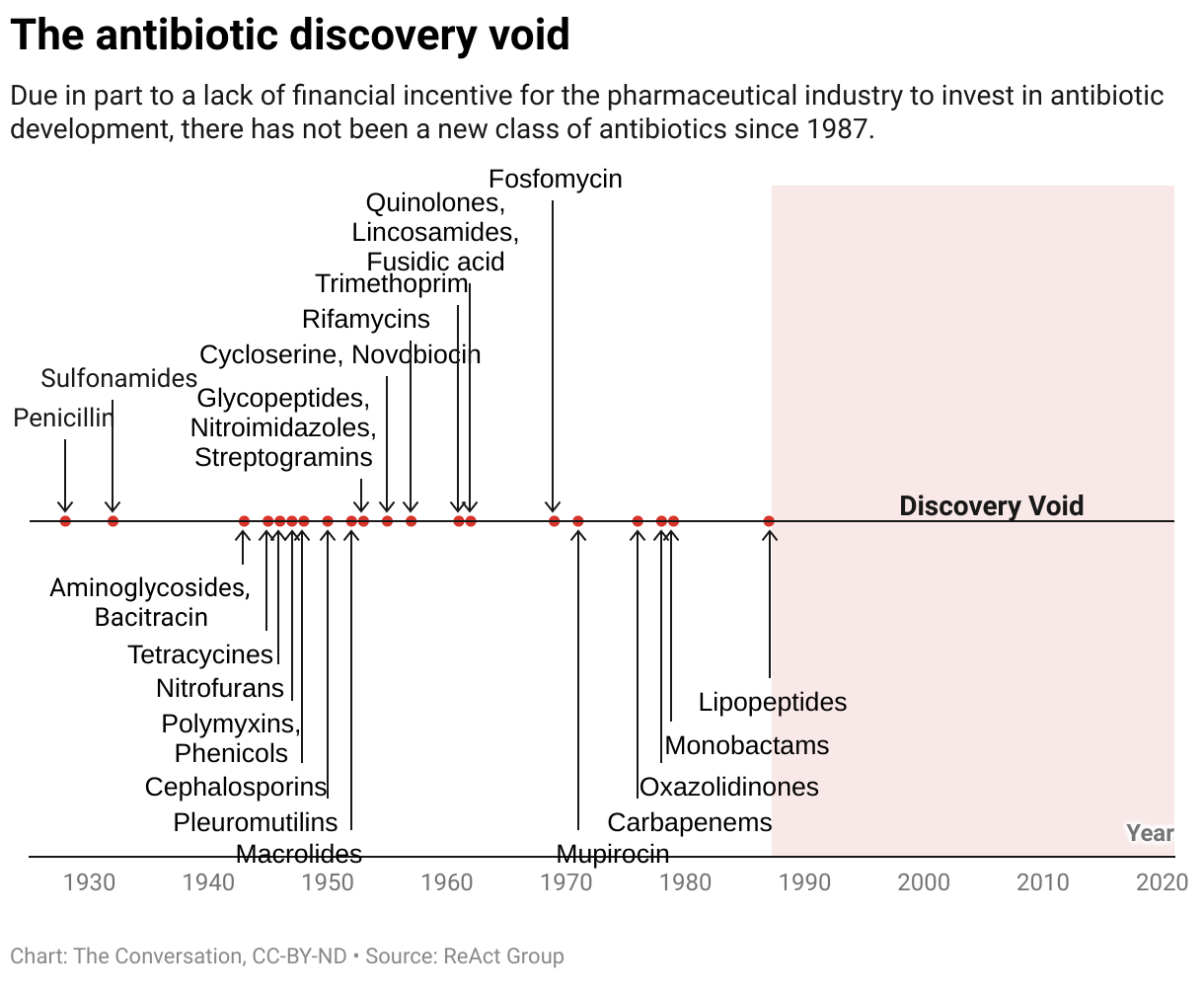
To remain forward, researchers are investing in nontraditional therapies, a lot of which work in essentially alternative ways than normal antibiotics.
One promising route is bacteriophage remedy, which makes use of viruses that particularly infect and kill dangerous micro organism. Others are exploring microbiome-based therapies that restore wholesome bacterial communities to crowd out pathogens.
Researchers are additionally creating CRISPR-based antimicrobials, utilizing gene-editing instruments to exactly disable resistance genes. New compounds like antimicrobial peptides, which puncture the membranes of micro organism to kill them, present promise as next-generation medication. In the meantime, scientists are designing nanoparticle supply techniques to move antimicrobials on to an infection websites with fewer unintended effects.
Past medication, scientists are analyzing ecological interventions to cut back the motion of resistance genes by means of soil, wastewater and plastics, in addition to by means of waterways and key environmental reservoirs.
Many of those choices stay early-stage, and micro organism might ultimately evolve round them. However these improvements replicate a robust shift: As an alternative of betting on discovering a single antibiotic to handle resistance, researchers are constructing a extra various and resilient instrument equipment to combat antibiotic-resistant pathogenic micro organism.
3. Antimicrobial resistance outdoors hospitals
Antibiotic resistance doesn’t solely unfold in hospitals. It strikes by means of individuals, wildlife, crops, wastewater, soil and world commerce networks. This broader perspective that takes the ideas of One Well being under consideration is crucial for understanding how resistance genes journey by means of ecosystems.
Researchers are more and more recognizing environmental and agricultural components as main drivers of resistance, on par with misuse of antibiotics within the clinic. These embrace how antibiotics utilized in animal agriculture can create resistant micro organism that unfold to individuals; how resistance genes in wastewater can survive remedy techniques and enter rivers and soil; and the way farms, sewage crops and different environmental sizzling spots develop into hubs the place resistance spreads rapidly. Even world journey accelerates the motion of resistant micro organism throughout continents inside hours.

Collectively, these forces present that antibiotic resistance isn’t simply a problem for hospitals – it’s an ecological and societal downside. For researchers, this implies designing options that cross disciplines, integrating microbiology, ecology, engineering, agriculture and public well being.
4. Insurance policies on what remedies exist sooner or later
Drug firms lose cash creating new antibiotics. As a result of new antibiotics are used sparingly with a view to protect their effectiveness, firms typically promote too few doses to recoup improvement prices even after the Meals and Drug Administration approves the medication. A number of antibiotic firms have gone bankrupt for that reason.
To encourage antibiotic innovation, the U.S. is contemplating main coverage modifications just like the PASTEUR Act. This bipartisan invoice proposes making a subscription-style cost mannequin that might permit the federal authorities as much as US$3 billion to pay drug producers over 5 to 10 years for entry to essential antibiotics as a substitute of paying per tablet.
World well being organizations, together with Médecins Sans Frontières (Medical doctors With out Borders), warning that the invoice ought to embrace stronger commitments to stewardship and equitable entry.
Nonetheless, the invoice represents one of the crucial vital coverage proposals associated to antimicrobial resistance in U.S. historical past and will decide what antibiotics exist sooner or later.
The way forward for antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is typically framed as an inevitable disaster. However I consider the fact is extra hopeful: Society is coming into an period of smarter diagnostics, modern therapies, ecosystem-level methods and coverage reforms geared toward rebuilding the antibiotic pipeline along with addressing stewardship.
For the general public, this implies higher instruments and stronger techniques of safety. For researchers and policymakers, it means collaborating in new methods.
The query now isn’t whether or not there are answers to antibiotic resistance – it’s whether or not society will act quick sufficient to make use of them.
This edited article is republished from The Dialog beneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the authentic article.