Pc-aided design (CAD) programs are tried-and-true instruments used to design lots of the bodily objects we use every day. However CAD software program requires intensive experience to grasp, and plenty of instruments incorporate such a excessive degree of element they don’t lend themselves to brainstorming or speedy prototyping.
In an effort to make design sooner and extra accessible for non-experts, researchers from MIT and elsewhere developed an AI-driven robotic meeting system that permits individuals to construct bodily objects by merely describing them in phrases.
Their system makes use of a generative AI mannequin to construct a 3D illustration of an object’s geometry primarily based on the person’s immediate. Then, a second generative AI mannequin causes concerning the desired object and figures out the place completely different elements ought to go, in line with the article’s operate and geometry.
The system can robotically construct the article from a set of prefabricated components utilizing robotic meeting. It might additionally iterate on the design primarily based on suggestions from the person.
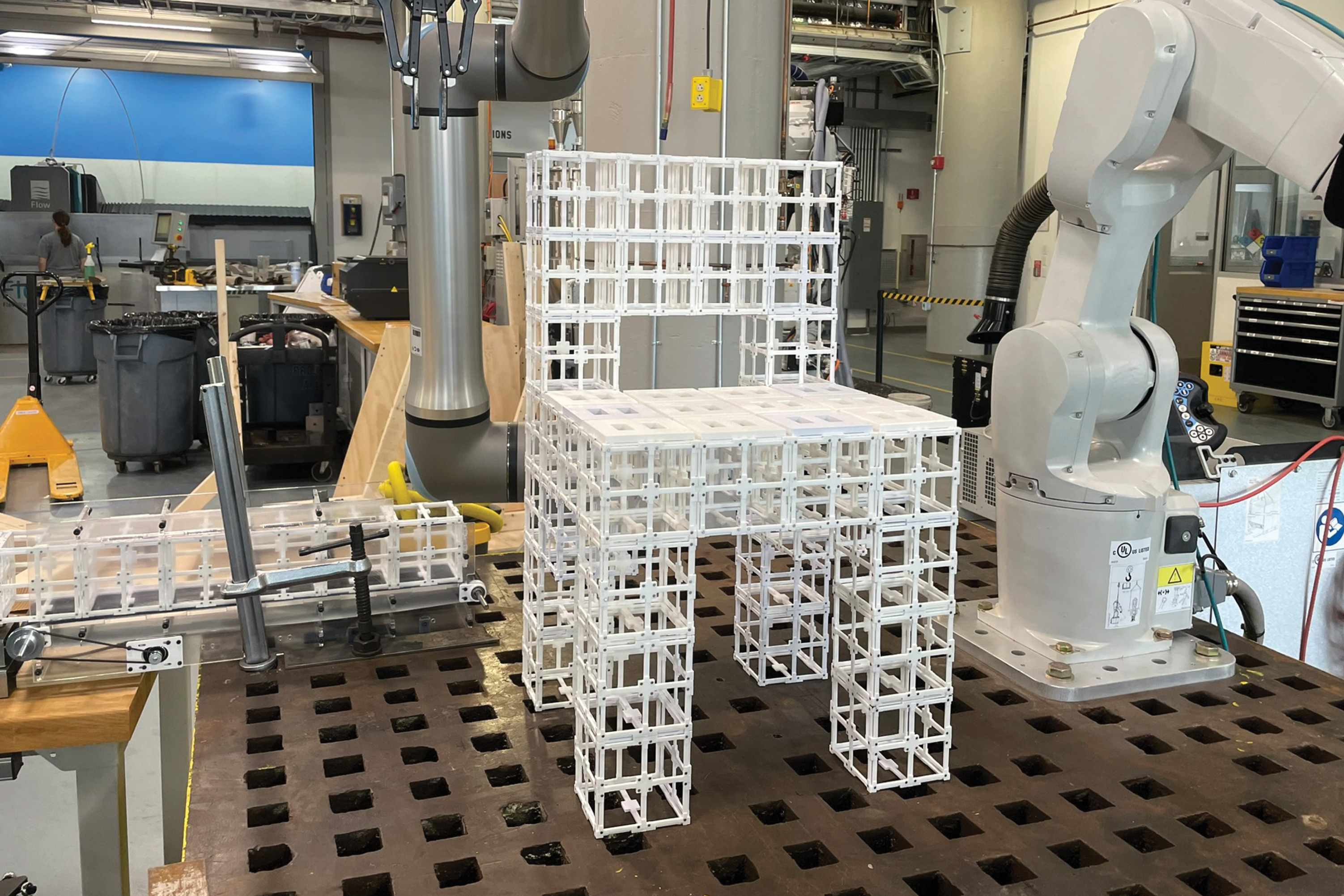
The researchers used this end-to-end system to manufacture furnishings, together with chairs and cabinets, from two sorts of premade elements. The elements will be disassembled and reassembled at will, decreasing the quantity of waste generated via the fabrication course of.
They evaluated these designs via a person examine and located that greater than 90 % of contributors most popular the objects made by their AI-driven system, as in comparison with completely different approaches.
Whereas this work is an preliminary demonstration, the framework may very well be particularly helpful for speedy prototyping advanced objects like aerospace elements and architectural objects. In the long run, it may very well be utilized in houses to manufacture furnishings or different objects regionally, with out the necessity to have cumbersome merchandise shipped from a central facility.
“In the end, we wish to have the ability to talk and discuss to a robotic and AI system the identical approach we discuss to one another to make issues collectively. Our system is a primary step towards enabling that future,” says lead creator Alex Kyaw, a graduate scholar within the MIT departments of Electrical Engineering and Pc Science (EECS) and Structure.
Kyaw is joined on the paper by Richa Gupta, an MIT structure graduate scholar; Faez Ahmed, affiliate professor of mechanical engineering; Lawrence Sass, professor and chair of the Computation Group within the Division of Structure; senior creator Randall Davis, an EECS professor and member of the Pc Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL); in addition to others at Google Deepmind and Autodesk Analysis. The paper was lately introduced on the Convention on Neural Data Processing Programs.
Producing a multicomponent design
Whereas generative AI fashions are good at producing 3D representations, often known as meshes, from textual content prompts, most don’t produce uniform representations of an object’s geometry which have the component-level particulars wanted for robotic meeting.
Separating these meshes into elements is difficult for a mannequin as a result of assigning elements relies on the geometry and performance of the article and its components.
The researchers tackled these challenges utilizing a vision-language mannequin (VLM), a strong generative AI mannequin that has been pre-trained to grasp photographs and textual content. They job the VLM with determining how two sorts of prefabricated components, structural elements and panel elements, ought to match collectively to type an object.
“There are a lot of methods we will put panels on a bodily object, however the robotic must see the geometry and motive over that geometry to decide about it. By serving as each the eyes and mind of the robotic, the VLM allows the robotic to do that,” Kyaw says.
A person prompts the system with textual content, maybe by typing “make me a chair,” and offers it an AI-generated picture of a chair to start out.
Then, the VLM causes concerning the chair and determines the place panel elements go on prime of structural elements, primarily based on the performance of many instance objects it has seen earlier than. As an illustration, the mannequin can decide that the seat and backrest ought to have panels to have surfaces for somebody sitting and leaning on the chair.
It outputs this info as textual content, similar to “seat” or “backrest.” Every floor of the chair is then labeled with numbers, and the knowledge is fed again to the VLM.
Then the VLM chooses the labels that correspond to the geometric components of the chair that ought to obtain panels on the 3D mesh to finish the design.
Human-AI co-design
The person stays within the loop all through this course of and may refine the design by giving the mannequin a brand new immediate, similar to “solely use panels on the backrest, not the seat.”
“The design house may be very huge, so we slim it down via person suggestions. We consider that is one of the best ways to do it as a result of individuals have completely different preferences, and constructing an idealized mannequin for everybody can be inconceivable,” Kyaw says.
“The human‑in‑the‑loop course of permits the customers to steer the AI‑generated designs and have a way of possession within the remaining outcome,” provides Gupta.
As soon as the 3D mesh is finalized, a robotic meeting system builds the article utilizing prefabricated components. These reusable components will be disassembled and reassembled into completely different configurations.
The researchers in contrast the outcomes of their technique with an algorithm that locations panels on all horizontal surfaces which are going through up, and an algorithm that locations panels randomly. In a person examine, greater than 90 % of people most popular the designs made by their system.
Additionally they requested the VLM to clarify why it selected to place panels in these areas.
“We realized that the imaginative and prescient language mannequin is ready to perceive some extent of the practical facets of a chair, like leaning and sitting, to grasp why it’s putting panels on the seat and backrest. It isn’t simply randomly spitting out these assignments,” Kyaw says.
Sooner or later, the researchers wish to improve their system to deal with extra advanced and nuanced person prompts, similar to a desk made out of glass and metallic. As well as, they wish to incorporate extra prefabricated elements, similar to gears, hinges, or different shifting components, so objects might have extra performance.
“Our hope is to drastically decrease the barrier of entry to design instruments. We’ve proven that we will use generative AI and robotics to show concepts into bodily objects in a quick, accessible, and sustainable method,” says Davis.