In an astonishing feat of gravitational sleuthing, astronomers have discovered a mysterious, dense blob of invisible matter embedded in a galaxy whose gentle took 7.3 billion years to succeed in us.
Precisely what this blob may be is at the moment an open query, but it surely’s completely tiny for the gap at which it was detected – simply round one million occasions the mass of the Solar. That is the smallest object to be discovered primarily based on gravity at giant cosmic distances, by an element of about 100.
“That is the lowest-mass object identified to us, by two orders of magnitude, to be detected at a cosmological distance by its gravitational impact,” explains a staff led by astrophysicist Devon Powell on the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Germany.
“This work demonstrates the observational feasibility of utilizing gravitational imaging to probe the million-solar-mass regime far past our native Universe.”
Associated: Mysterious Darkish Matter Mapped Throughout Area Like By no means Earlier than
frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
Primarily based on our observations of the Universe, there’s one thing on the market that emits no gentle and solely interacts with the remainder of the Universe by way of gravity.
We name this one thing darkish matter, and there are a number of candidate explanations for what it may be. The consistency of the matter – whether or not it is easy or clumpy – might help scientists slim it down. Nonetheless, as a result of darkish matter emits no gentle, mapping its distribution is difficult.
This brings us to gravity. Every part within the Universe with mass causes spacetime to bend round it – the larger the mass, the larger the spacetime curvature. Think about placing, say, a bowling ball on a trampoline. When you roll a marble throughout the stretched trampoline mat, it should observe the curved path across the bowling ball.
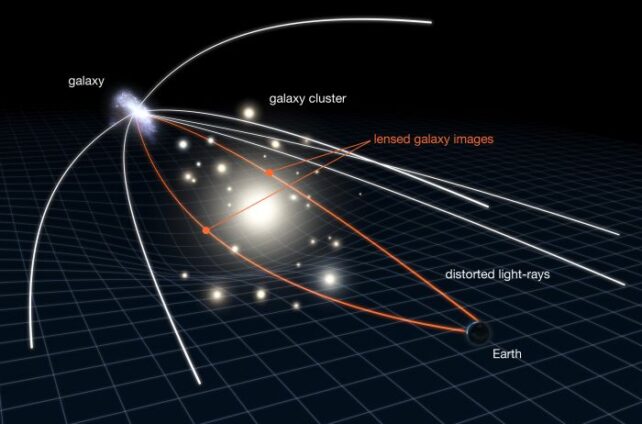
Now think about the bowling ball is a galaxy and the marble is a photon. A set of photons from a distant galaxy touring by way of the spacetime warped by the gravity of a more in-depth galaxy (the bowling ball) will attain us stretched, distorted, and magnified. That is what we name a gravitational lens.
These lenses are an excellent device for learning the distant Universe, since they amplify deep house in a means that know-how can not. However astronomers also can use that stretched and distorted distant gentle to map the distribution of matter within the foreground lens.
That is what Powell and his colleagues got down to do, utilizing an in depth community of telescopes, together with the Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope, the Very Lengthy Baseline Array, and the European Very Lengthy Baseline Interferometric Community, to residence in on a well known gravitational lens system referred to as JVAS B1938+666.
This method consists of a foreground galaxy at a light-travel time of about 7.3 billion years, and a extra distant galaxy at roughly 10.5 billion years’ light-travel time whose gentle grew to become stretched and quadrupled by the foreground galaxy.
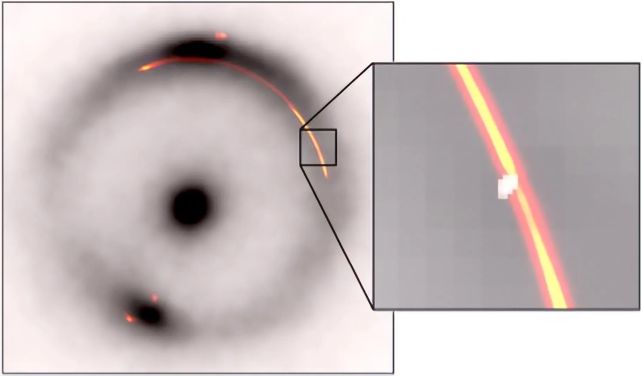
One of many photos of the lensed galaxy is a brilliant, smeared arc of sunshine; in that smeared arc, the researchers discovered a pinched type of dimple. This pinch, the researchers ascertained, couldn’t have been created by the lensing galaxy alone. As an alternative, the offender needs to be a clump of mass, a willpower made with a whopping confidence degree of 26 sigma.
“From the primary high-resolution picture, we instantly noticed a narrowing within the gravitational arc, which is the tell-tale signal that we had been onto one thing,” says astronomer John McKean of the College of Groningen within the Netherlands.
“Solely one other small clump of mass between us and the distant radio galaxy might trigger this.”
The mass emits no gentle – not in optical, radio, or infrared wavelengths. It is both utterly darkish or far too dim to see. Because of this there are a number of issues it might be. The main candidates are a clump of darkish matter or a dwarf galaxy that emits too little gentle for us to detect.
Both choice is believable right now, and additional analysis efforts are wanted to find out the id of the offender.
“Given the sensitivity of our information, we had been anticipating to seek out at the very least one darkish object, so our discovery is in keeping with the so-called ‘chilly darkish matter principle’ on which a lot of our understanding of how galaxies type is predicated,” Powell says.
“Having discovered one, the query now could be whether or not we are able to discover extra and whether or not their quantity will nonetheless agree with the fashions.”
The findings have been detailed in companion papers printed in Nature Astronomy and the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.


