The Mills ratio [1] is the ratio of the CCDF to the PDF. That’s, for a random variable X, the Mills ratio at x is the complementary cumulative distribution perform divided by the density perform. If the density perform of X is f, then
The Mills ratio highlights an necessary distinction between the Pupil t distribution and the conventional distribution.
Introductory statistics courses will say issues like “you possibly can approximate a t distribution with a standard if it has greater than 30 levels of freedom.” Which may be true, relying on the appliance. A t(30) distribution and a standard distribution behave equally within the center however not within the tails.
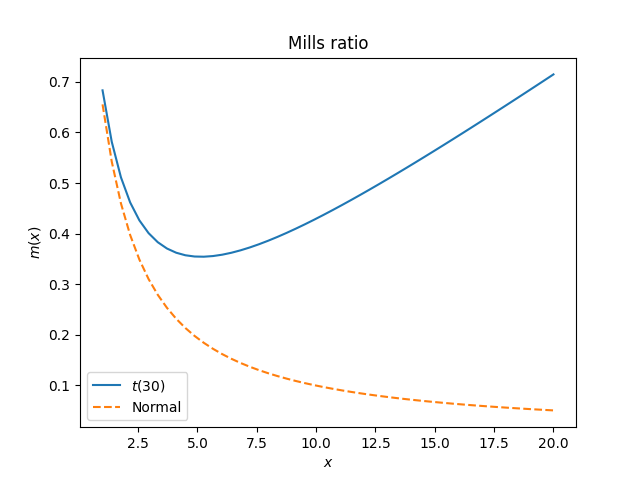
The Mills ratio for a t distribution with ν levels of freedom is asymptotically x/ν, whereas the Mills ratio for the standard regular distribution is asymptotically 1/x. Observe that rising ν does make the Mills perform smaller, nevertheless it nonetheless ultimately grows linearly whereas the Mills perform of a standard distribution decays linearly.
Usually, the Mills ratio is a reducing perform for thin-tailed distributions and an rising perform for fat-tailed distributions. The exponential distribution is within the center, with fixed Mills perform.
Associated posts
[1] Named after John P. Mills, so there’s no apostrophe earlier than the s.
